Indigo dye creates the distinctive deep blue hue in denim with a natural, uneven fade that enhances the fabric's character over time. Sulphur dye produces darker, black or grey shades and offers better colorfastness but fades more uniformly compared to indigo. Choosing between indigo and sulphur dye impacts the denim's appearance, durability, and aging process.
Table of Comparison
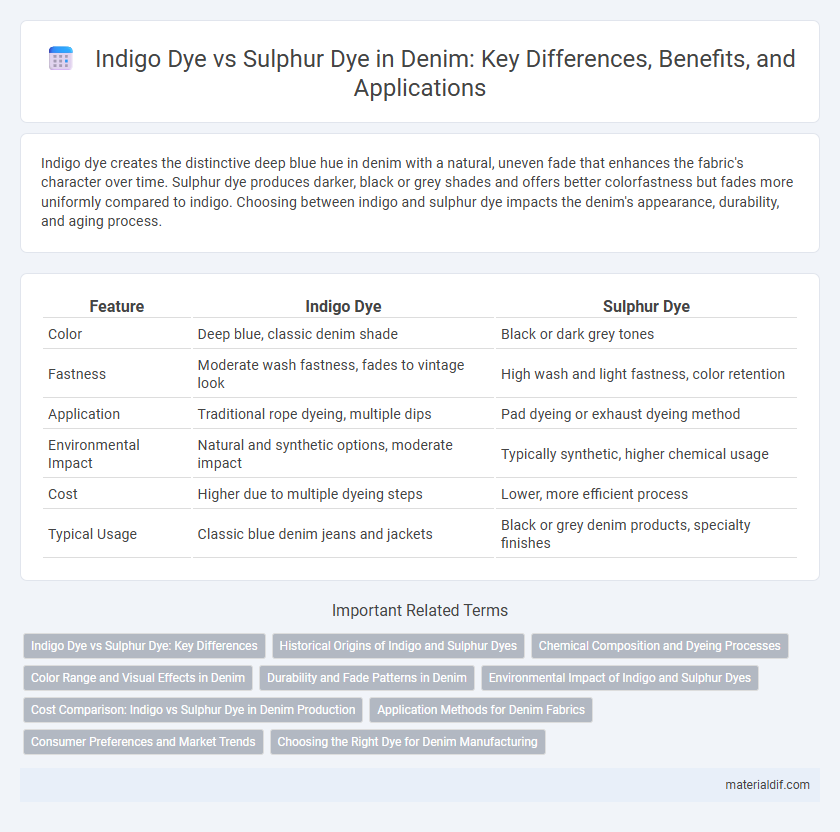
| Feature | Indigo Dye | Sulphur Dye |
|---|---|---|
| Color | Deep blue, classic denim shade | Black or dark grey tones |
| Fastness | Moderate wash fastness, fades to vintage look | High wash and light fastness, color retention |
| Application | Traditional rope dyeing, multiple dips | Pad dyeing or exhaust dyeing method |
| Environmental Impact | Natural and synthetic options, moderate impact | Typically synthetic, higher chemical usage |
| Cost | Higher due to multiple dyeing steps | Lower, more efficient process |
| Typical Usage | Classic blue denim jeans and jackets | Black or grey denim products, specialty finishes |
Indigo Dye vs Sulphur Dye: Key Differences
Indigo dye, derived from the Indigofera plant, creates the classic deep blue hue characteristic of denim, while sulphur dye produces darker shades like black and gray through a chemical process involving sulfur compounds. Indigo dye adheres primarily to the surface of cotton fibers, resulting in a fading effect that enhances denim's vintage and worn-in look, whereas sulphur dye penetrates the fiber, offering permanent color but less fading over time. The environmental impact differs as well; traditional indigo dyeing can involve water-intensive processes, but sulphur dyes often require fewer resources and generate less wastewater, influencing sustainable denim production choices.
Historical Origins of Indigo and Sulphur Dyes
Indigo dye, derived from the Indigofera plant, has been used for over 6,000 years, with origins tracing back to ancient civilizations in India and Mesopotamia, renowned for its vibrant blue color in textile dyeing. Sulphur dye, developed in the 20th century, revolutionized denim production with its cost-effective and durable black and dark brown hues, originating from chemical processes rather than natural sources. The historical significance of indigo dye lies in its natural extraction and cultural heritage, while sulphur dye represents industrial innovation in denim manufacturing.
Chemical Composition and Dyeing Processes
Indigo dye, primarily composed of indigotin molecules, undergoes a reduction-oxidation process involving vat dyeing where the fabric is submerged in a reduced, soluble form and exposed to air for color fixation. Sulphur dye consists of sulfur compounds and organosulfur substances, applied through a hot alkaline bath that facilitates dye penetration and bonding with cellulose fibers via covalent bonds formed during oxidation. The distinct chemical properties influence fastness, shade range, and environmental impact in denim dyeing applications.
Color Range and Visual Effects in Denim
Indigo dye produces the classic deep blue hue synonymous with traditional denim, offering rich color depth and natural fading patterns that enhance the garment's vintage appeal. Sulphur dye expands the color range to include blacks, greys, and warmer tones, providing versatile options for contemporary denim styles with unique matte or glossy finishes. The choice between indigo and sulphur dyes directly influences the visual texture and aging characteristics, defining the denim's overall aesthetic and wear experience.
Durability and Fade Patterns in Denim
Indigo dye in denim is renowned for its superior durability, allowing the fabric to maintain deep blue hues while developing unique fade patterns that enhance with wear, creating a personalized aesthetic. Sulphur dye, often used for black or grey denim, offers a more uniform fade but generally exhibits less resistance to abrasion, leading to quicker wear and less distinct fading. The choice between indigo and sulphur dye significantly impacts the longevity and visual evolution of denim garments.
Environmental Impact of Indigo and Sulphur Dyes
Indigo dye, primarily derived from natural plant sources or synthetic indigo, tends to have a lower environmental impact due to its biodegradability and lower toxicity compared to sulphur dyes, which often release harmful sulfur compounds during production and disposal. Sulphur dyes, commonly used for their affordability and colorfastness in denim manufacturing, contribute significantly to water pollution and pose challenges in wastewater treatment due to their complex chemical structure and sulfur-based pollutants. The sustainable choice in denim dyeing heavily favors indigo dye, especially when sourced or produced with eco-friendly methods, reducing the ecological footprint associated with water contamination and chemical waste.
Cost Comparison: Indigo vs Sulphur Dye in Denim Production
Indigo dye remains more expensive than sulphur dye in denim production due to its complex extraction from indigo plants or synthetic production, which drives up raw material costs and labor intensity. Sulphur dye offers a cost-effective alternative with lower raw material prices and simpler application processes, making it popular for budget-conscious manufacturers aiming for darker color variations. The cost efficiency of sulphur dye contributes to reduced overall production expenses, although it may lack the depth and fading characteristics intrinsic to traditional indigo-dyed denim.
Application Methods for Denim Fabrics
Indigo dye is primarily applied to denim through rope dyeing and ring dyeing techniques, where the yarns are repeatedly dipped in indigo dye baths to build up a rich, deep color with a characteristic fade over time. Sulphur dye is typically used for achieving black or gray shades on denim and is applied via exhaust dyeing, offering faster penetration and more uniform coloration but with less pronounced fading effects. The choice between indigo and sulphur dye application methods impacts the denim's final appearance, wear characteristics, and washing treatments required.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Indigo dye remains the dominant choice in denim production due to its iconic deep blue hue and natural fading characteristics, which appeal to consumers seeking authentic vintage styles. Sulphur dye, gaining traction for its versatility in producing black, gray, and other shades, attracts a growing segment of buyers looking for modern and sustainable color options. Market trends indicate an increasing demand for eco-friendly processes, with consumers favoring brands that use low-impact sulphur dye techniques alongside traditional indigo to balance heritage and innovation in denim fashion.
Choosing the Right Dye for Denim Manufacturing
Indigo dye imparts the classic deep blue hue synonymous with traditional denim, offering excellent colorfastness and unique fading patterns that enhance garment character over time. Sulphur dye provides a broader color spectrum, including blacks and greys, with superior wash durability and cost-effective scalability for mass production. Selecting the right dye depends on the desired aesthetic, production volume, and fabric performance, with indigo favored for heritage styles and sulphur dye optimal for contemporary, versatile denim collections.
Indigo Dye vs Sulphur Dye Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com