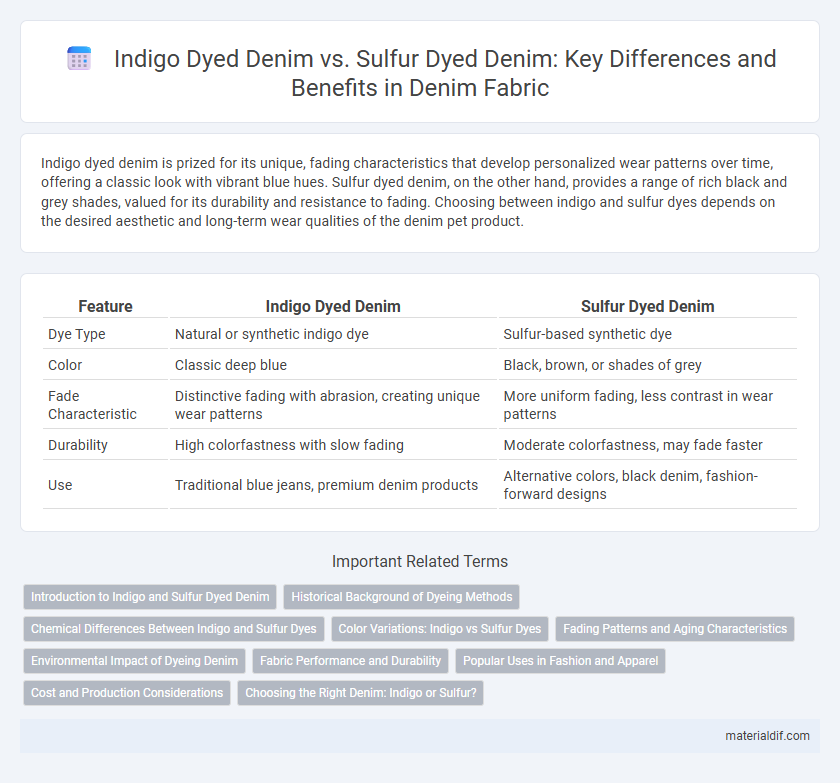
Indigo dyed denim is prized for its unique, fading characteristics that develop personalized wear patterns over time, offering a classic look with vibrant blue hues. Sulfur dyed denim, on the other hand, provides a range of rich black and grey shades, valued for its durability and resistance to fading. Choosing between indigo and sulfur dyes depends on the desired aesthetic and long-term wear qualities of the denim pet product.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Indigo Dyed Denim | Sulfur Dyed Denim |
|---|---|---|
| Dye Type | Natural or synthetic indigo dye | Sulfur-based synthetic dye |
| Color | Classic deep blue | Black, brown, or shades of grey |
| Fade Characteristic | Distinctive fading with abrasion, creating unique wear patterns | More uniform fading, less contrast in wear patterns |
| Durability | High colorfastness with slow fading | Moderate colorfastness, may fade faster |
| Use | Traditional blue jeans, premium denim products | Alternative colors, black denim, fashion-forward designs |
Introduction to Indigo and Sulfur Dyed Denim
Indigo dyed denim is characterized by its deep blue hue achieved through repeated dipping in indigo dye, which adheres to the fiber surface producing a unique fade over time. Sulfur dyed denim, in contrast, employs sulfur-based dyes that grant a range of colors such as black, gray, and olive, offering more color variety compared to traditional indigo. Both techniques influence denim's texture, durability, and aesthetic appeal, making them fundamental in denim manufacturing and fashion trends.
Historical Background of Dyeing Methods
Indigo dyed denim has origins dating back to the late 19th century, gaining prominence due to its vibrant blue hue achieved through a natural dye extracted from the Indigofera plant. Sulfur dyed denim emerged in the mid-20th century as an economical alternative, providing a range of darker shades from black to olive green using sulfur compounds in the dyeing process. The historical evolution of these dyeing methods reflects shifts in textile technology and consumer preferences within the denim industry.
Chemical Differences Between Indigo and Sulfur Dyes
Indigo dye is a vat dye consisting of insoluble leucoindigo, which penetrates denim fibers and oxidizes upon exposure to air, creating its signature deep blue hue. Sulfur dye, derived from sulfur and organic compounds, produces colors ranging from black to brown and binds to fibers through a reduction-oxidation reaction that is less vibrant but more colorfast than indigo. The chemical structure of indigo allows for fading and distressing effects typical in denim fashion, whereas sulfur dyes provide more uniform, durable coloration without significant fading.
Color Variations: Indigo vs Sulfur Dyes
Indigo dyed denim exhibits rich, deep blue hues that fade uniquely with wear, creating classic vintage appeal and distinctive color variations over time. Sulfur dyed denim offers a broader spectrum of colors, including black, brown, green, and gray, with a more solid, less faded appearance compared to indigo. The chemical properties of indigo allow surface dyeing, producing a characteristic fade pattern, whereas sulfur dyes penetrate fibers differently, resulting in more uniform coloration.
Fading Patterns and Aging Characteristics
Indigo dyed denim exhibits distinctive fading patterns characterized by high contrast between deep blue hues and crisp white highlights along creases and edges, creating a vintage, worn-in look over time. Sulfur dyed denim, often found in black or gray tones, fades more uniformly with subtle, muted aging, producing gentle grayish undertones rather than stark contrasts. These aging characteristics make indigo denim popular for those seeking bold, dynamic fades, while sulfur dyed denim appeals to those preferring understated and less pronounced wear patterns.
Environmental Impact of Dyeing Denim
Indigo dyed denim primarily uses natural or synthetic indigo dye, which can require significant water and chemical use during the dyeing and rinsing processes, impacting freshwater resources if not managed properly. Sulfur dyed denim involves sulfur-based dyes that typically consume less water and energy, but the chemicals used may generate harmful byproducts requiring careful wastewater treatment to prevent environmental contamination. Sustainable practices such as closed-loop water systems and eco-friendly dye alternatives are crucial to reducing the environmental footprint of both indigo and sulfur dyed denim production.
Fabric Performance and Durability
Indigo dyed denim is renowned for its superior colorfastness and ability to develop unique fading patterns over time, enhancing fabric performance with increased breathability and softness due to the dye sitting on the yarn surface. Sulfur dyed denim offers excellent durability and resistance to UV light and abrasion, making it ideal for heavy-duty usage, but it tends to have less vibrant color and lower breathability compared to indigo. Both dyeing methods significantly impact the fabric's longevity, with indigo favored for aesthetic aging effects and sulfur preferred for robust wear and longevity.
Popular Uses in Fashion and Apparel
Indigo dyed denim is predominantly used in classic blue jeans, jackets, and casual wear due to its traditional look and unique fading properties that enhance garment character over time. Sulfur dyed denim features a broader color range, including blacks and greys, making it popular in streetwear and contemporary fashion for a sleek, modern aesthetic. Both dyeing techniques cater to distinct fashion demands, with indigo favored for heritage styles and sulfur preferred for versatile, trend-driven apparel.
Cost and Production Considerations
Indigo dyed denim typically incurs higher production costs due to the complex dyeing process involving multiple dips to achieve the characteristic deep blue color, resulting in longer production times and increased water usage. Sulfur dyed denim offers a more cost-effective alternative with faster dyeing processes and lower material expenses, often producing colors like black, brown, or olive, but may lack the fading and aging qualities associated with indigo. Manufacturers weigh these factors when selecting dye types to balance cost efficiency and desired aesthetic outcomes in denim production.
Choosing the Right Denim: Indigo or Sulfur?
Indigo dyed denim features deep blue hues with a distinctive fading pattern that enhances over time, making it ideal for classic, vintage-inspired styles. Sulfur dyed denim offers a broader color palette including black, grey, and khaki tones, providing versatility for modern and contemporary fashion. Selecting the right denim depends on desired aesthetics and durability, with indigo emphasizing traditional fading and sulfur delivering stable, solid colors.
Indigo Dyed Denim vs Sulfur Dyed Denim Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com