Certified cotton ensures adherence to strict environmental and social standards, promoting sustainable farming practices and fair labor conditions. Non-certified cotton often lacks transparency, increasing risks of pesticide overuse and worker exploitation. Choosing certified cotton supports eco-friendly production and contributes to ethical supply chains.
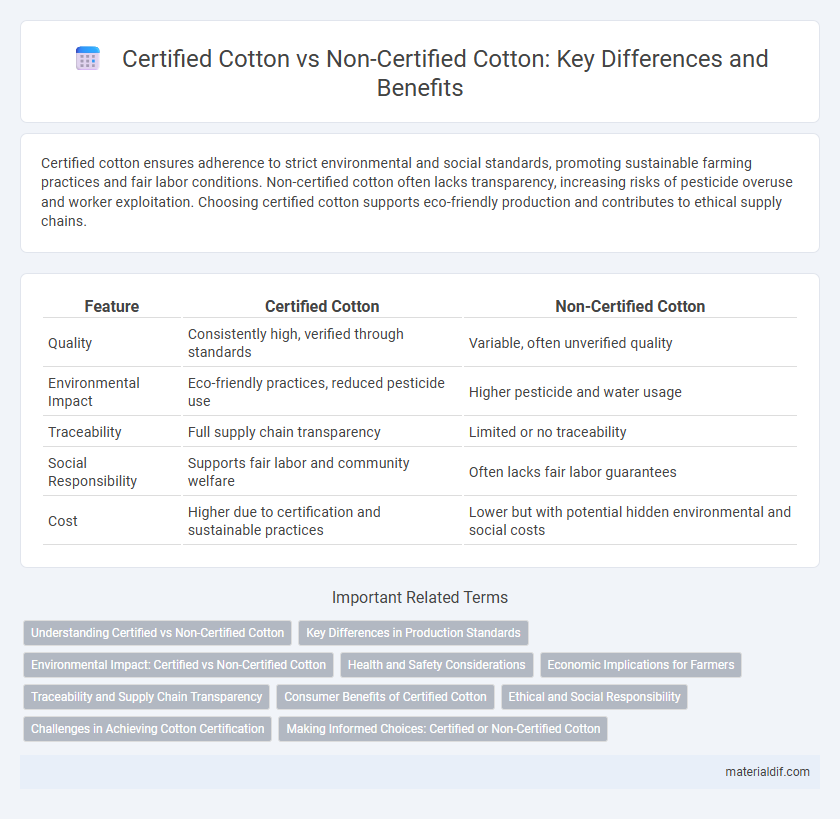
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Certified Cotton | Non-Certified Cotton |
|---|---|---|
| Quality | Consistently high, verified through standards | Variable, often unverified quality |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly practices, reduced pesticide use | Higher pesticide and water usage |
| Traceability | Full supply chain transparency | Limited or no traceability |
| Social Responsibility | Supports fair labor and community welfare | Often lacks fair labor guarantees |
| Cost | Higher due to certification and sustainable practices | Lower but with potential hidden environmental and social costs |
Understanding Certified vs Non-Certified Cotton
Certified cotton undergoes rigorous verification processes ensuring sustainable farming practices, traceability, and reduced environmental impact, attracting consumers prioritizing ethical sourcing. Non-certified cotton lacks these formal validations, which may result in variable farming practices, potentially higher pesticide use, and uncertain supply chain transparency. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for brands aiming to support sustainable agriculture and meet growing consumer demand for responsible textile production.
Key Differences in Production Standards
Certified cotton adheres to strict environmental and social criteria, including reduced pesticide use, sustainable water management, and fair labor practices, ensuring traceability and transparency throughout the supply chain. Non-certified cotton often lacks standardized oversight, which can lead to higher chemical usage, inconsistent quality, and potential labor violations. The key differences in production standards impact the overall sustainability, safety, and ethical considerations associated with the cotton fiber.
Environmental Impact: Certified vs Non-Certified Cotton
Certified cotton significantly reduces environmental impact through sustainable farming practices that minimize water usage, pesticide application, and soil degradation compared to non-certified cotton. Non-certified cotton often relies on conventional methods with heavy chemical inputs, leading to higher pollution levels and increased carbon emissions. Adoption of certified cotton supports biodiversity conservation and promotes healthier ecosystems by adhering to strict environmental standards.
Health and Safety Considerations
Certified cotton undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it is free from harmful chemicals and pesticides, significantly reducing health risks for both farmers and consumers. Non-certified cotton often involves the use of toxic substances that can cause allergic reactions, skin irritations, and long-term health issues due to residual chemicals. Choosing certified cotton supports safer agricultural practices and provides a cleaner, hypoallergenic product safer for sensitive skin and overall health.
Economic Implications for Farmers
Certified cotton often commands higher market prices due to its adherence to sustainable and ethical standards, providing farmers with increased income and access to premium markets. Non-certified cotton typically faces lower demand and price volatility, limiting farmers' earning potential and financial stability. Investing in certification processes can lead to long-term economic benefits by enhancing market competitiveness and fostering consumer trust.
Traceability and Supply Chain Transparency
Certified cotton offers enhanced traceability throughout the supply chain, ensuring that every stage from farm to fabric meets established environmental and social standards. Non-certified cotton often lacks comprehensive documentation, making it difficult to verify sustainable practices or labor conditions. Supply chain transparency in certified cotton boosts consumer trust and supports ethical sourcing initiatives by providing clear provenance and accountability.
Consumer Benefits of Certified Cotton
Certified cotton ensures consumers receive higher-quality, sustainable products verified by reputable standards such as GOTS or OEKO-TEX, reducing exposure to harmful pesticides and chemicals. This certification supports environmentally responsible farming practices and fair labor conditions, promoting ethical consumption and social accountability. Choosing certified cotton enhances product durability and comfort, providing long-term value and peace of mind for eco-conscious shoppers.
Ethical and Social Responsibility
Certified cotton ensures adherence to strict environmental and social standards, promoting fair wages, safe working conditions, and sustainable farming practices. Non-certified cotton often lacks transparency, potentially associating with exploitative labor and harmful pesticides usage. Choosing certified cotton supports ethical supply chains and fosters social responsibility in the textile industry.
Challenges in Achieving Cotton Certification
Achieving cotton certification involves overcoming significant challenges such as stringent compliance with environmental standards, traceability requirements, and labor practices verification. Farmers often face high costs and complexity in adopting sustainable farming techniques necessary for certified cotton status. Limited access to resources and education further complicates the transition from non-certified to certified cotton production.
Making Informed Choices: Certified or Non-Certified Cotton
Certified cotton ensures adherence to sustainable farming practices, reduced pesticide use, and fair labor conditions, offering transparency and traceability for eco-conscious consumers. Non-certified cotton may vary widely in environmental impact and ethical standards, lacking verified assurances, which can lead to greater ecological footprint and social concerns. Making informed choices requires evaluating supply chain credibility, production methods, and certifications like Organic, Fair Trade, or GOTS to prioritize sustainability and social responsibility.
Certified Cotton vs Non-Certified Cotton Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com