Glazed ceramics feature a smooth, glass-like coating that enhances durability, stain resistance, and aesthetic appeal by providing a glossy finish. Unglazed ceramics have a porous surface that offers better slip resistance and a natural, matte look but can be more susceptible to stains and moisture absorption. Choosing between glazed and unglazed ceramics depends on the intended use, preferred texture, and maintenance requirements.
Table of Comparison
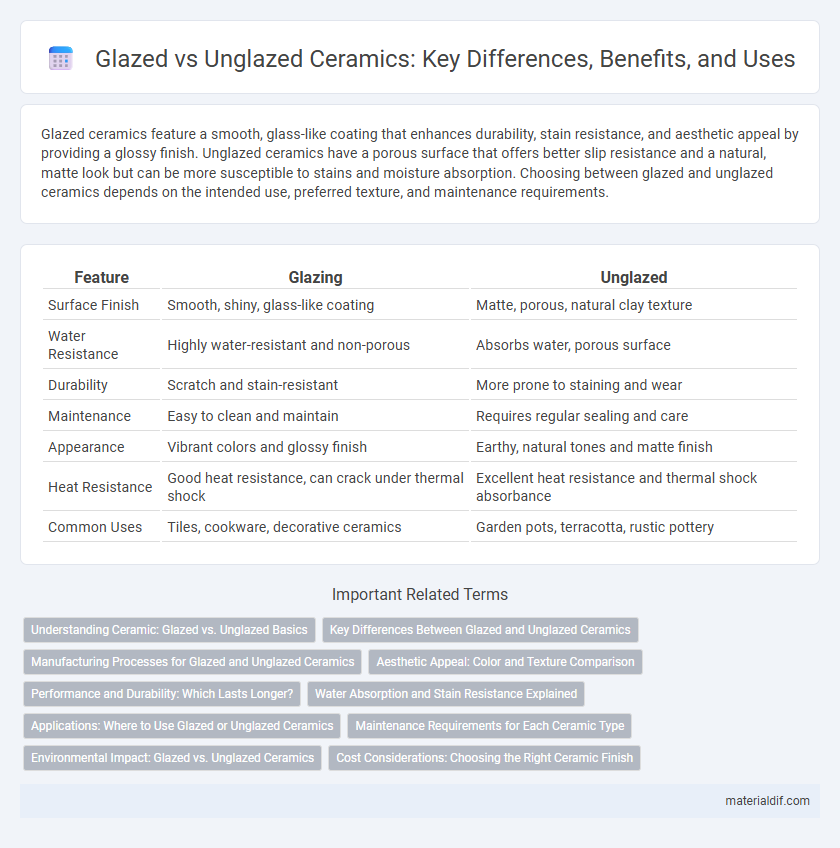
| Feature | Glazing | Unglazed |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Finish | Smooth, shiny, glass-like coating | Matte, porous, natural clay texture |
| Water Resistance | Highly water-resistant and non-porous | Absorbs water, porous surface |
| Durability | Scratch and stain-resistant | More prone to staining and wear |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean and maintain | Requires regular sealing and care |
| Appearance | Vibrant colors and glossy finish | Earthy, natural tones and matte finish |
| Heat Resistance | Good heat resistance, can crack under thermal shock | Excellent heat resistance and thermal shock absorbance |
| Common Uses | Tiles, cookware, decorative ceramics | Garden pots, terracotta, rustic pottery |
Understanding Ceramic: Glazed vs. Unglazed Basics
Glazed ceramics feature a glassy, non-porous surface created by applying and firing a liquid glaze, enhancing durability, water resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Unglazed ceramics remain porous and matte, offering better breathability and a natural, tactile texture often preferred for functional pottery like terracotta. Choosing between glazed and unglazed depends on factors such as moisture exposure, desired finish, and intended use, impacting maintenance and longevity.
Key Differences Between Glazed and Unglazed Ceramics
Glazed ceramics feature a glassy coating that enhances durability, waterproofing, and aesthetic appeal, while unglazed ceramics maintain a porous surface that absorbs moisture and offers a natural texture. The glaze chemically bonds during kiln firing, creating a non-porous barrier resistant to stains and scratches, whereas unglazed ceramics are more prone to damage but allow better breathability for applications like plant pots. In terms of maintenance, glazed ceramics are easier to clean and more hygienic, whereas unglazed ceramics may require sealing to prevent staining and moisture absorption.
Manufacturing Processes for Glazed and Unglazed Ceramics
Glazed ceramics undergo a manufacturing process where a liquid glass coating is applied and fused onto the surface through high-temperature firing, enhancing durability, water resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Unglazed ceramics are fired without this coating, resulting in a porous, matte finish that requires specialized production controls to ensure structural integrity and prevent cracking. The glazing process involves additional steps such as glaze formulation, application techniques, and controlled kiln atmospheres, while unglazed ceramics rely heavily on precise clay body composition and firing schedules to achieve desired strength and texture.
Aesthetic Appeal: Color and Texture Comparison
Glazing enhances ceramic surfaces by adding vibrant colors and a glossy finish that intensifies visual depth and richness. Unglazed ceramics offer a natural, matte texture with subtle earthy tones, emphasizing raw material qualities and a tactile, organic appeal. The choice impacts aesthetic preference, with glazing suited for bold, reflective designs and unglazed favored for understated, textured artistry.
Performance and Durability: Which Lasts Longer?
Glazed ceramics feature a glass-like coating that enhances resistance to stains, scratches, and moisture, significantly improving their durability compared to unglazed ceramics. Unglazed ceramics, while offering better slip resistance and a natural texture, are more porous and susceptible to wear, leading to faster degradation under heavy use. For long-lasting performance, glazed ceramics provide superior protection and longevity in both residential and commercial applications.
Water Absorption and Stain Resistance Explained
Glazed ceramics feature a glass-like coating that significantly reduces water absorption, enhancing stain resistance by creating a non-porous surface. Unglazed ceramics, being more porous, absorb more water and are prone to staining, requiring sealing for protection. Lower porosity in glazed tiles improves durability and hygiene, making them ideal for areas exposed to moisture and spills.
Applications: Where to Use Glazed or Unglazed Ceramics
Glazed ceramics are ideal for applications requiring water resistance, stain protection, and enhanced aesthetic appeal, such as bathroom tiles, kitchenware, and decorative pottery. Unglazed ceramics excel in environments needing durability and slip resistance, making them suitable for floor tiles, industrial components, and outdoor paving. Selecting between glazed and unglazed ceramics depends on the specific functional requirements like moisture exposure, wear resistance, and desired surface texture.
Maintenance Requirements for Each Ceramic Type
Glazed ceramics require less frequent cleaning due to their smooth, non-porous surface that resists stains and moisture, making them ideal for high-traffic areas or kitchens. Unglazed ceramics, being porous, demand regular sealing and more intensive cleaning to prevent absorption of liquids and dirt, which can lead to staining and wear. Maintenance for glazed ceramics is generally simpler, involving mild detergents, whereas unglazed ceramics benefit from specialized products to maintain their structural integrity and appearance.
Environmental Impact: Glazed vs. Unglazed Ceramics
Glazed ceramics create a protective, non-porous surface that often requires higher firing temperatures, increasing energy consumption and carbon emissions during production. Unglazed ceramics, being more porous, typically demand lower firing temperatures, resulting in a smaller carbon footprint and reduced environmental impact. However, glazed ceramics offer improved durability and stain resistance, potentially extending product lifespan and offsetting initial environmental costs.
Cost Considerations: Choosing the Right Ceramic Finish
Glazed ceramic surfaces typically incur higher costs due to additional materials and labor required for the glazing process, including kiln firings and quality control. Unglazed ceramics offer a more budget-friendly alternative, often used in applications where aesthetics are less critical or a natural texture is preferred. Evaluating long-term durability and maintenance expenses is vital when deciding between glazed and unglazed finishes to ensure cost-effectiveness over time.
Glazing vs Unglazed Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com