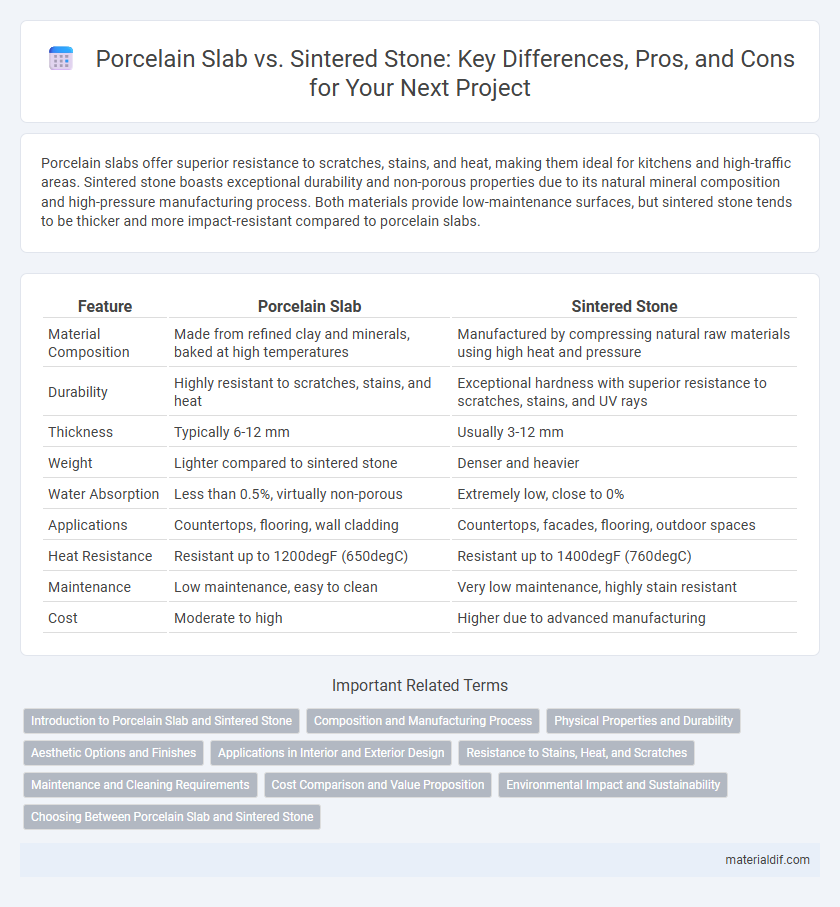
Porcelain slabs offer superior resistance to scratches, stains, and heat, making them ideal for kitchens and high-traffic areas. Sintered stone boasts exceptional durability and non-porous properties due to its natural mineral composition and high-pressure manufacturing process. Both materials provide low-maintenance surfaces, but sintered stone tends to be thicker and more impact-resistant compared to porcelain slabs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Porcelain Slab | Sintered Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Made from refined clay and minerals, baked at high temperatures | Manufactured by compressing natural raw materials using high heat and pressure |
| Durability | Highly resistant to scratches, stains, and heat | Exceptional hardness with superior resistance to scratches, stains, and UV rays |
| Thickness | Typically 6-12 mm | Usually 3-12 mm |
| Weight | Lighter compared to sintered stone | Denser and heavier |
| Water Absorption | Less than 0.5%, virtually non-porous | Extremely low, close to 0% |
| Applications | Countertops, flooring, wall cladding | Countertops, facades, flooring, outdoor spaces |
| Heat Resistance | Resistant up to 1200degF (650degC) | Resistant up to 1400degF (760degC) |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to clean | Very low maintenance, highly stain resistant |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Higher due to advanced manufacturing |
Introduction to Porcelain Slab and Sintered Stone
Porcelain slabs are engineered stone products made from refined clay and minerals, fired at high temperatures to achieve exceptional hardness, low porosity, and resistance to stains and scratches. Sintered stone, created through a sintering process involving extreme heat and pressure, boasts superior durability, UV resistance, and is composed of natural minerals such as quartz and feldspar. Both materials are popular choices for countertops and flooring, offering outstanding aesthetic versatility and long-term performance in residential and commercial applications.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Porcelain slabs are crafted from a blend of kaolin, feldspar, quartz, and clay, which are compressed at extremely high pressures and fired at temperatures exceeding 1200degC, resulting in a dense, non-porous surface. Sintered stone is produced through a high-pressure, high-temperature process called sintering, combining natural minerals such as quartz, feldspar, and silica without melting them, yielding a highly durable and UV-resistant material. The primary difference lies in the manufacturing process: porcelain slabs undergo vitrification, whereas sintered stone is formed by sintering raw materials in a solid-state, enhancing strength and resistance.
Physical Properties and Durability
Porcelain slabs exhibit high resistance to thermal shock, low water absorption below 0.05%, and hardness ranked at 6-7 on the Mohs scale, making them suitable for various indoor and outdoor applications. Sintered stone offers enhanced durability with a denser composition, exceptional scratch and UV resistance, and fireproof qualities, often demonstrating a Mohs hardness of 7-8. Both materials provide excellent resistance to staining and chemical agents, but sintered stone typically surpasses porcelain slabs in mechanical strength and long-term weather durability.
Aesthetic Options and Finishes
Porcelain slabs offer a wide range of aesthetic options, including polished, matte, and textured finishes that mimic natural stone or concrete with high color consistency and resistance to fading. Sintered stone provides exceptional visual depth and a more varied, natural appearance with finishes such as honed, leathered, and ultra-matte, showcasing intricate mineral patterns and organic textures. Both materials deliver durable surface solutions, but sintered stone stands out for its ability to replicate complex natural stone aesthetics with unique finishes.
Applications in Interior and Exterior Design
Porcelain slabs offer superior water resistance and versatility, making them ideal for kitchen countertops, bathroom surfaces, and outdoor patios due to their low porosity and durability against weather elements. Sintered stone excels in high-traffic interior flooring, wall cladding, and commercial facades because of its enhanced strength, UV resistance, and scratch-proof properties. Both materials provide aesthetic appeal with varied finishes and patterns, but porcelain slabs generally perform better in wet environments while sintered stone is preferred for heavy-duty exterior applications.
Resistance to Stains, Heat, and Scratches
Porcelain slabs offer excellent resistance to stains, heat, and scratches due to their dense, non-porous surface and high firing temperatures. Sintered stone, created through a high-pressure and heat process, provides superior durability with enhanced resistance against chemical stains, extreme heat, and abrasion. Both materials are highly resilient, but sintered stone typically outperforms porcelain slabs in scratch and heat resistance for demanding applications.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Porcelain slabs require minimal maintenance due to their non-porous surface, making them resistant to stains, scratches, and bacteria buildup, and they can be easily cleaned with mild detergents and water. Sintered stone also offers low maintenance, featuring high durability and resistance to heat, chemicals, and UV rays, but it may require specialized cleaning products to preserve its surface integrity. Both materials are ideal for high-traffic areas, with porcelain slabs being slightly more user-friendly for everyday cleaning.
Cost Comparison and Value Proposition
Porcelain slabs typically cost between $50 and $100 per square foot, offering a durable and stain-resistant option suitable for various applications. Sintered stone, priced from $60 to $120 per square foot, provides superior scratch resistance and heat tolerance, adding long-term value despite the higher initial investment. Comparing cost and performance, sintered stone delivers enhanced durability and aesthetics, making it a valuable choice for premium projects requiring longevity and minimal maintenance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Porcelain slabs and sintered stone both offer eco-friendly alternatives to traditional stone, with porcelain slabs made from natural clay and minerals requiring lower water and energy during manufacturing. Sintered stone boasts exceptional durability and resistance to chemical agents, extending product lifespan and reducing the need for replacement. Both materials are recyclable and produced with minimal waste, making them sustainable choices for environmentally conscious construction and design projects.
Choosing Between Porcelain Slab and Sintered Stone
Porcelain slabs offer exceptional hardness and stain resistance, making them ideal for high-traffic areas and outdoor use, while sintered stone provides superior heat resistance and UV stability, perfect for surfaces exposed to extreme conditions. Both materials exhibit low porosity and durability, but porcelain's dense structure excels in moisture-prone environments, whereas sintered stone's mineral-based composition ensures longevity against scratches and thermal shock. Choosing between porcelain slab and sintered stone depends on specific application needs, such as exposure to elements, expected wear, and aesthetic preferences.
Porcelain Slab vs Sintered Stone Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com