Basalt and bluestone are both dense, durable natural stones frequently used in construction and landscaping, but they differ in composition and appearance. Basalt, a volcanic igneous rock, typically features a dark gray to black color with a fine-grained texture, making it highly resistant to weathering and ideal for outdoor applications like paving and cladding. Bluestone, often a sandstone or limestone variant, offers a blue-gray hue with a smoother surface and slightly softer texture, preferred for patios, walkways, and decorative features that require a more polished aesthetic.
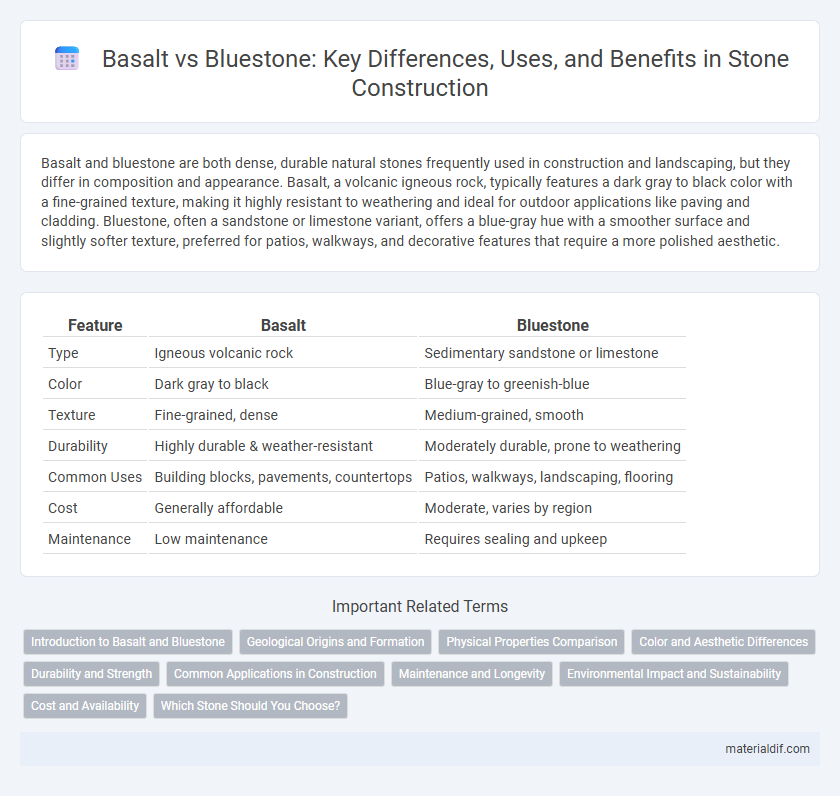
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Basalt | Bluestone |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Igneous volcanic rock | Sedimentary sandstone or limestone |
| Color | Dark gray to black | Blue-gray to greenish-blue |
| Texture | Fine-grained, dense | Medium-grained, smooth |
| Durability | Highly durable & weather-resistant | Moderately durable, prone to weathering |
| Common Uses | Building blocks, pavements, countertops | Patios, walkways, landscaping, flooring |
| Cost | Generally affordable | Moderate, varies by region |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Requires sealing and upkeep |
Introduction to Basalt and Bluestone
Basalt is a dense, fine-grained volcanic rock known for its durability and dark gray to black coloration, commonly used in construction and landscaping. Bluestone, a natural sandstone with a distinctive blue-gray hue, is prized for its aesthetic appeal and versatility in paving and architectural applications. Both stones offer unique physical properties, making them suitable for various design and structural purposes.
Geological Origins and Formation
Basalt is an igneous volcanic rock formed from the rapid cooling of basaltic lava, characterized by its fine-grained texture and high iron and magnesium content. Bluestone, often a sedimentary rock such as sandstone or limestone, forms through the compaction and cementation of mineral particles over millions of years in marine or riverine environments. The geological origins highlight basalt's volcanic activity compared to bluestone's sedimentary deposition processes, influencing their distinct physical properties and uses in construction.
Physical Properties Comparison
Basalt is a dense, fine-grained volcanic rock characterized by high durability and a dark, uniform color, often ranging from black to dark gray. Bluestone, a type of sandstone, exhibits a medium density with a distinctive blue-gray hue and layered texture, offering moderate strength and weather resistance. The compressive strength of basalt typically exceeds that of bluestone, making basalt more suitable for heavy-duty applications requiring superior hardness and wear resistance.
Color and Aesthetic Differences
Basalt exhibits a rich, deep black or dark gray hue, presenting a sleek, modern aesthetic ideal for contemporary designs. Bluestone offers a softer palette with blue-gray tones that sometimes include hints of purple and green, lending a more natural and rustic appeal. The color variation in bluestone creates dynamic visual interest, while basalt's consistent dark shade emphasizes minimalism and elegance.
Durability and Strength
Basalt exhibits superior durability and strength compared to bluestone due to its fine-grained volcanic origin, making it resistant to weathering and heavy wear. Bluestone, typically composed of sandstone or limestone, offers moderate durability but is more prone to chipping and erosion under harsh conditions. For construction projects requiring high load-bearing capacity and longevity, basalt is often the preferred choice over bluestone.
Common Applications in Construction
Basalt is commonly used in construction for road base, concrete aggregate, and railway ballast due to its durability and high compressive strength. Bluestone finds frequent application in patios, walkways, and building facades, valued for its natural blue-gray color and smooth texture. Both stones provide excellent durability, but basalt's hardness makes it ideal for heavy-duty infrastructure, while bluestone is preferred for decorative and architectural purposes.
Maintenance and Longevity
Basalt offers superior durability and low maintenance due to its dense, non-porous structure, making it highly resistant to weathering and staining. Bluestone requires more regular sealing and upkeep to prevent surface erosion and discoloration over time, especially in high-traffic areas. For long-term projects demanding minimal maintenance, basalt is often the more sustainable and long-lasting choice.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Basalt and bluestone differ significantly in their environmental impact and sustainability, with basalt typically sourced through more energy-efficient quarrying methods that reduce carbon emissions. Bluestone, although durable, often requires intensive processing and transportation due to limited local availability, leading to a higher overall carbon footprint. Choosing basalt contributes to lower ecological disruption and supports sustainable construction practices by leveraging its abundant natural reserves and minimal processing requirements.
Cost and Availability
Basalt generally costs more than bluestone due to its denser composition and limited quarry locations, impacting its availability. Bluestone is widely available in the northeastern United States, often making it a more budget-friendly option for landscaping and construction projects. Cost differences between basalt and bluestone are influenced by regional quarry accessibility and transportation expenses.
Which Stone Should You Choose?
Basalt offers superior durability and a dense composition, making it ideal for heavy-traffic outdoor areas, while bluestone provides a smoother texture and a more uniform color palette suited for patios and walkways. Both stones are natural and weather-resistant, but basalt's volcanic origin gives it enhanced strength and heat resistance compared to the softer, sedimentary bluestone. Choosing between basalt and bluestone depends on the specific project requirements, with basalt preferred for strength and longevity, and bluestone favored for aesthetic versatility and ease of maintenance.
Basalt vs Bluestone Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com