Addition cure silicone offers superior dimensional stability and faster curing times compared to condensation cure silicone, making it ideal for precise applications. Condensation cure silicone releases alcohol as a byproduct during curing, which can cause shrinkage and affect accuracy. Choice between the two depends on project requirements, with addition cure preferred for high-precision molds and condensation cure suited for less critical applications due to its lower cost.
Table of Comparison
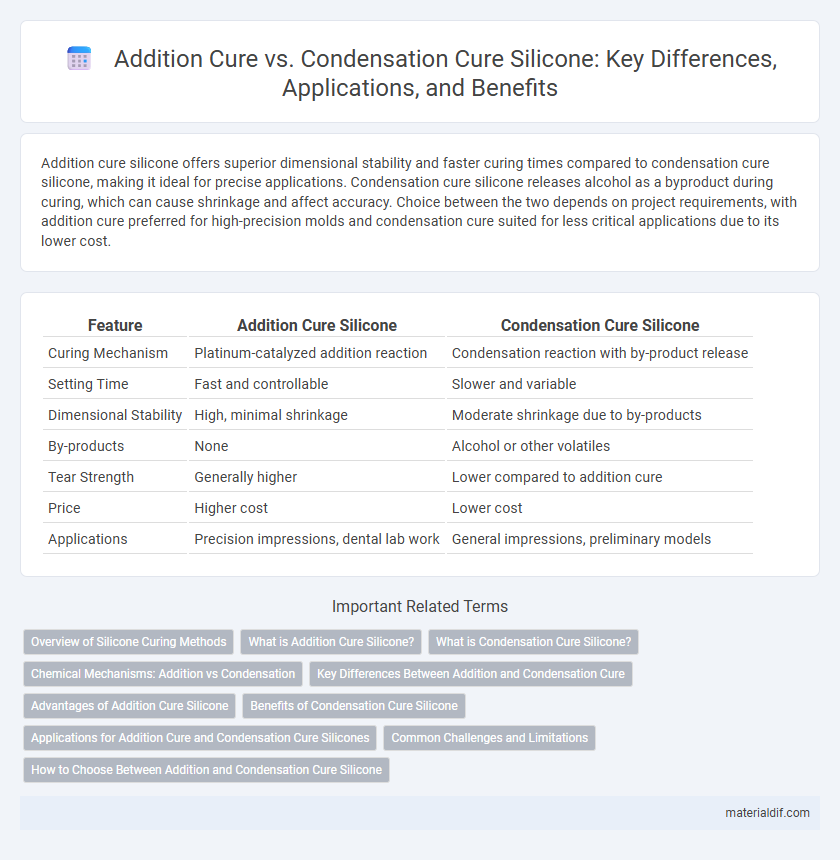
| Feature | Addition Cure Silicone | Condensation Cure Silicone |
|---|---|---|
| Curing Mechanism | Platinum-catalyzed addition reaction | Condensation reaction with by-product release |
| Setting Time | Fast and controllable | Slower and variable |
| Dimensional Stability | High, minimal shrinkage | Moderate shrinkage due to by-products |
| By-products | None | Alcohol or other volatiles |
| Tear Strength | Generally higher | Lower compared to addition cure |
| Price | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Applications | Precision impressions, dental lab work | General impressions, preliminary models |
Overview of Silicone Curing Methods
Addition cure silicones, also known as platinum-catalyzed silicones, cure through a hydrosilylation reaction involving vinyl and hydride groups, resulting in low shrinkage and excellent mechanical properties. Condensation cure silicones utilize a condensation reaction between silanol groups and alkoxy or acetoxy groups, often releasing by-products like alcohol or acetic acid during the curing process. Addition cure systems are preferred for precision applications due to superior dimensional stability, whereas condensation cure silicones are valued for their ease of use and cost-effectiveness in less critical sealing and molding tasks.
What is Addition Cure Silicone?
Addition cure silicone is a type of silicone elastomer formed through a platinum-catalyzed reaction between vinyl and hydride groups, resulting in a precise and stable polymer network without releasing by-products. This curing process provides exceptional dimensional stability, biocompatibility, and resistance to tearing, making it ideal for medical, dental, and high-precision molding applications. Unlike condensation cure silicone, addition cure offers superior mechanical properties and long-term durability due to its absence of shrinkage and volatile by-products during polymerization.
What is Condensation Cure Silicone?
Condensation cure silicone is a type of silicone elastomer that hardens through a chemical reaction between silicone polymers and a cross-linking agent, typically releasing by-products such as alcohol or acetic acid during curing. This curing process generally occurs at room temperature, making it suitable for applications like mold making, dental impressions, and prototyping. Compared to addition cure silicones, condensation cure silicones often exhibit lower dimensional stability but offer easier processing and compatibility with various substrates.
Chemical Mechanisms: Addition vs Condensation
Addition cure silicones polymerize through a platinum-catalyzed reaction where vinyl groups and hydrosilane crosslinkers form a stable, inert network without byproducts. Condensation cure silicones undergo a hydrolysis and condensation process, releasing small molecules like alcohol or water as byproducts during polymer chain formation. The differing mechanisms influence cure speed, shrinkage, and mechanical properties, with addition cure offering superior dimensional stability and biocompatibility.
Key Differences Between Addition and Condensation Cure
Addition cure silicones undergo polymerization through a platinum-catalyzed reaction that produces no byproducts, resulting in higher dimensional stability and less shrinkage compared to condensation cure silicones. Condensation cure silicones release byproducts such as alcohol during curing, which can cause more shrinkage and limit their use in precision applications. The choice between addition cure and condensation cure depends on the required accuracy, mechanical properties, and application environment.
Advantages of Addition Cure Silicone
Addition cure silicone offers superior dimensional stability and faster curing times compared to condensation cure silicone, minimizing shrinkage and distortion in dental and industrial applications. It provides enhanced biocompatibility and resistance to tearing, making it ideal for precision impressions and molds. Its low odor and shelf stability further contribute to user-friendly handling and reliable results.
Benefits of Condensation Cure Silicone
Condensation cure silicone offers superior flexibility and faster curing times compared to addition cure silicone, making it ideal for applications requiring rapid processing. Its ability to cure in the presence of moisture provides enhanced adhesion to diverse substrates, ensuring strong and durable bonds. The cost-effectiveness and lower sensitivity to contaminants further distinguish condensation cure silicone as a practical solution for industrial sealing and molding applications.
Applications for Addition Cure and Condensation Cure Silicones
Addition cure silicones are widely used in dental impressions, electronic encapsulation, and medical device manufacturing due to their superior dimensional stability and low shrinkage. Condensation cure silicones find applications in sealants, mold making for prototyping, and general-purpose adhesives where moderate accuracy and flexible curing conditions are acceptable. Choosing between addition cure and condensation cure silicones depends on the required precision, cure time, and mechanical properties for specific industrial or medical applications.
Common Challenges and Limitations
Addition cure silicones often face challenges with inhibition caused by contaminants such as sulfur, amines, or latex, which can prevent proper curing and result in tacky surfaces. Condensation cure silicones have limitations related to shrinkage and longer curing times due to the release of alcohol byproducts, impacting dimensional stability. Both types can exhibit sensitivity to moisture, but condensation cure silicones are generally more prone to degradation and decreased mechanical properties over time.
How to Choose Between Addition and Condensation Cure Silicone
Choosing between addition cure and condensation cure silicone depends on the application's precision and durability requirements. Addition cure silicone offers superior dimensional stability and strength, ideal for detailed molds and medical devices, while condensation cure silicone is more flexible and cost-effective, suitable for general-purpose sealing and prototyping. Consider the cure time, shrinkage rate, and environmental resistance to match the silicone type with your specific project needs.
Addition Cure vs Condensation Cure Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com