Linen warp threads run lengthwise on the loom and provide the fabric with strength and stability, while linen weft threads run crosswise and influence the texture and flexibility of the finished material. Warp threads are typically stronger and smoother because they must withstand tension during weaving, whereas weft threads can be softer and more decorative. The interplay between the linen warp and weft determines the overall durability, appearance, and feel of the textile.
Table of Comparison
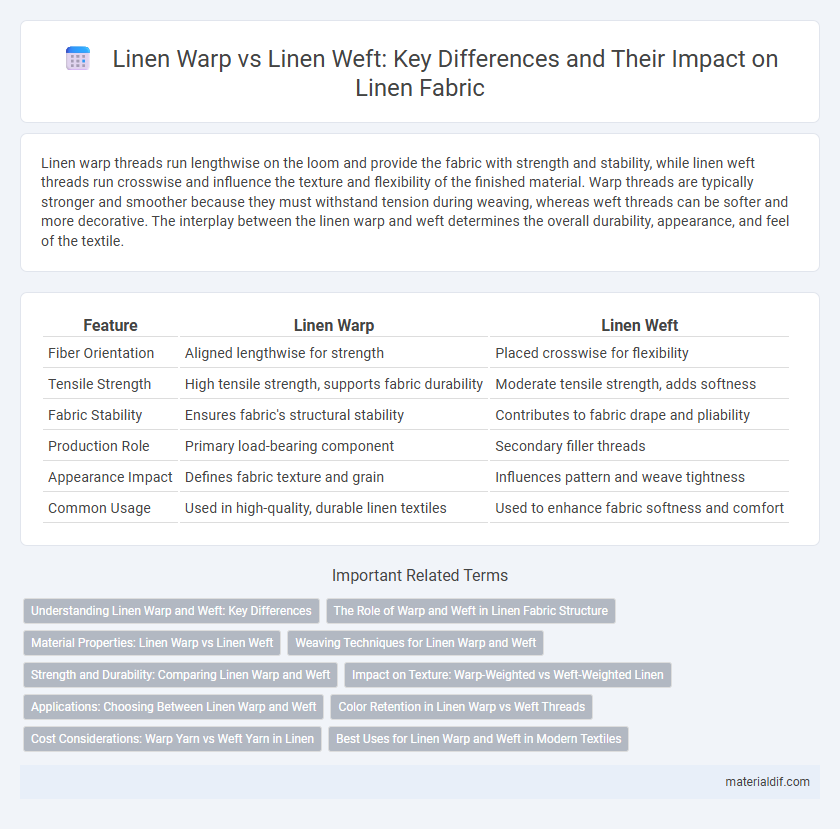
| Feature | Linen Warp | Linen Weft |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Orientation | Aligned lengthwise for strength | Placed crosswise for flexibility |
| Tensile Strength | High tensile strength, supports fabric durability | Moderate tensile strength, adds softness |
| Fabric Stability | Ensures fabric's structural stability | Contributes to fabric drape and pliability |
| Production Role | Primary load-bearing component | Secondary filler threads |
| Appearance Impact | Defines fabric texture and grain | Influences pattern and weave tightness |
| Common Usage | Used in high-quality, durable linen textiles | Used to enhance fabric softness and comfort |
Understanding Linen Warp and Weft: Key Differences
Linen warp fibers run lengthwise on the loom, providing strength and stability to the fabric, while linen weft fibers weave crosswise, influencing texture and flexibility. Warp threads are typically smoother and more tension-resistant to maintain fabric shape, whereas weft threads can be looser, allowing for more variation in surface and feel. Understanding these differences is essential for optimizing linen fabric durability, appearance, and functionality in textile production.
The Role of Warp and Weft in Linen Fabric Structure
In linen fabric, the warp yarns run lengthwise and provide the structural strength and stability essential for durability in weaving. The weft yarns interlace horizontally across the warp, contributing to fabric flexibility and texture, creating the characteristic crispness and breathability of linen. Together, these yarns balance tension and resilience, defining the unique tactile qualities and long-lasting performance of linen textiles.
Material Properties: Linen Warp vs Linen Weft
Linen warp threads are typically stronger and finer, providing the fabric with durability and structural integrity, while linen weft threads tend to be thicker and more textured, contributing to the fabric's softness and flexibility. The difference in fiber orientation during spinning results in warp yarns having higher tensile strength and less elasticity, enhancing the fabric's resistance to stretching. Conversely, weft yarns offer better absorbency and breathability, improving comfort in linen textiles.
Weaving Techniques for Linen Warp and Weft
Linen warp fibers, chosen for their strength and durability, are aligned longitudinally on the loom to provide a stable foundation for weaving, while linen weft fibers, typically softer and more flexible, interlace transversely to create texture and pattern. Weaving techniques for linen emphasize maintaining tension in the warp threads to prevent distortion, using methods such as plain weave or twill to highlight the natural luster and strength of linen fibers. The interplay between the coarse linen warp and finer linen weft enhances fabric resilience and breathability, essential qualities in linen textiles.
Strength and Durability: Comparing Linen Warp and Weft
Linen warp fibers are typically stronger and more durable than linen weft fibers due to their longitudinal alignment and tension during weaving. Warp threads must withstand continuous tension on the loom, resulting in tighter, more resilient yarns that enhance fabric strength. In contrast, weft threads, woven perpendicular to the warp, generally exhibit less stress and consequently lower tensile strength and durability.
Impact on Texture: Warp-Weighted vs Weft-Weighted Linen
Linen warp threads, typically stronger and more tensioned, create warp-weighted fabric with a firm, crisp texture ideal for durable textiles and structured garments. The weft threads, often softer and looser, generate weft-weighted linen characterized by a softer, more pliable texture suited for lightweight, breathable clothing. Warp-weighted linen emphasizes rigidity and longevity, while weft-weighted linen enhances comfort and drape in finished fabric.
Applications: Choosing Between Linen Warp and Weft
Linen warp fibers provide superior strength and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty textiles like upholstery and canvas. Linen weft fibers offer greater flexibility and softness, suited for lightweight fabrics such as apparel and fine linens. Selecting between linen warp and weft depends on the desired textile characteristics and end-use applications.
Color Retention in Linen Warp vs Weft Threads
Linen warp threads typically exhibit stronger color retention compared to weft threads due to their higher tension and alignment during the weaving process, which enhances dye absorption and fixation. Weft threads, woven across the warp, often undergo more abrasion and flexing, leading to faster color fading over time. The distinct fiber orientation and weaving dynamics between warp and weft critically influence the durability and vibrancy of linen fabrics.
Cost Considerations: Warp Yarn vs Weft Yarn in Linen
Linen warp yarn typically incurs higher costs than weft yarn due to its greater length, strength, and uniformity requirements essential for fabric durability. The spinning process for warp yarn demands finer, more consistent fibers to withstand tension during weaving, resulting in increased production expenses. Weft yarn, subjected to less stress, can be coarser and less uniform, making it generally more affordable in linen fabric manufacturing.
Best Uses for Linen Warp and Weft in Modern Textiles
Linen warp threads, known for their strength and durability, are ideal for creating the foundational structure in modern textiles such as upholstery and heavy-duty home furnishings where longevity is key. Linen weft fibers, which tend to be softer and more flexible, excel in lightweight garments and fine linens that require comfort and breathability. Combining sturdy linen warp with supple linen weft enhances fabric performance in contemporary fashion and interior design by balancing resilience with softness.
Linen Warp vs Linen Weft Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com