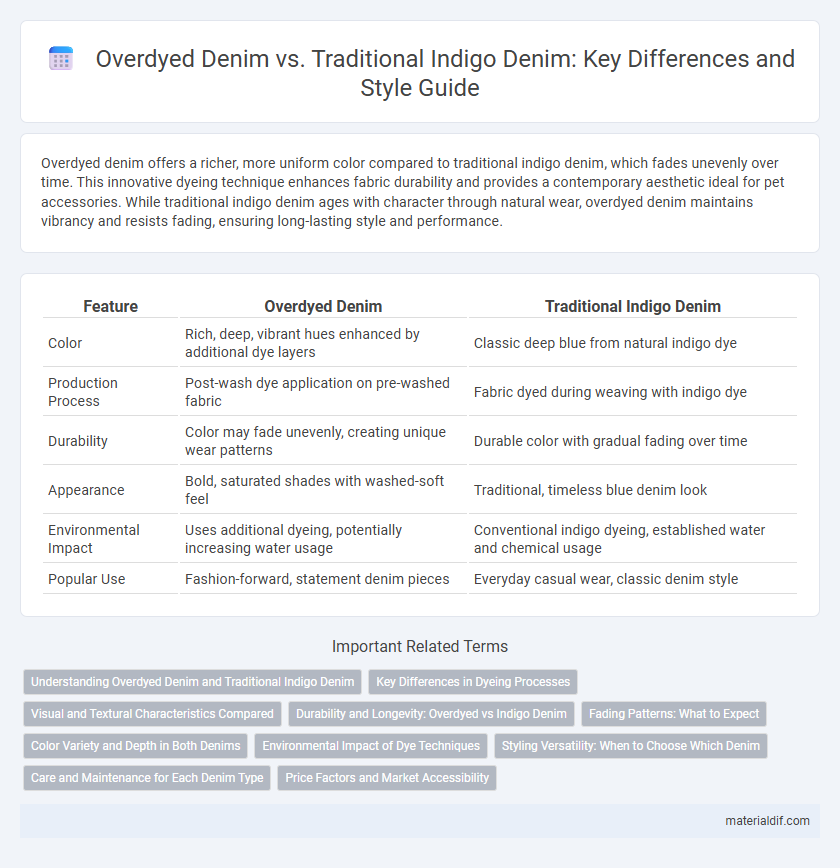
Overdyed denim offers a richer, more uniform color compared to traditional indigo denim, which fades unevenly over time. This innovative dyeing technique enhances fabric durability and provides a contemporary aesthetic ideal for pet accessories. While traditional indigo denim ages with character through natural wear, overdyed denim maintains vibrancy and resists fading, ensuring long-lasting style and performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Overdyed Denim | Traditional Indigo Denim |
|---|---|---|
| Color | Rich, deep, vibrant hues enhanced by additional dye layers | Classic deep blue from natural indigo dye |
| Production Process | Post-wash dye application on pre-washed fabric | Fabric dyed during weaving with indigo dye |
| Durability | Color may fade unevenly, creating unique wear patterns | Durable color with gradual fading over time |
| Appearance | Bold, saturated shades with washed-soft feel | Traditional, timeless blue denim look |
| Environmental Impact | Uses additional dyeing, potentially increasing water usage | Conventional indigo dyeing, established water and chemical usage |
| Popular Use | Fashion-forward, statement denim pieces | Everyday casual wear, classic denim style |
Understanding Overdyed Denim and Traditional Indigo Denim
Overdyed denim involves re-dyeing finished or washed denim fabrics to achieve rich, vibrant colors beyond the classic blue shades found in traditional indigo denim, which is colored through the natural indigo dyeing process of cotton fibers. Traditional indigo denim undergoes multiple dips in indigo dye vats, creating its signature fading and aging patterns unique to wear over time, while overdyed denim offers an innovative approach to color customization and depth. Understanding the differences highlights overdyed denim's versatility in fashion-forward designs, contrasting with the heritage appeal and timeless durability of indigo-dyed denim.
Key Differences in Dyeing Processes
Overdyed denim undergoes a secondary dyeing process where a solid color is applied over the initial indigo or other base color, creating a richer, often darker or uniquely tinted fabric. Traditional indigo denim relies on repeated dipping of the yarns in indigo dye baths, which gradually builds up the signature blue color through oxidization and results in a distinctive fading pattern with wear. The key difference lies in overdyed denim's post-weaving coloration that alters the fabric's surface color, whereas traditional indigo dyeing focuses on yarn-level color development before weaving.
Visual and Textural Characteristics Compared
Overdyed denim features richer, often more varied hues achieved through additional dye layers that enhance color intensity and depth, resulting in a unique, sometimes mottled visual texture compared to traditional indigo denim's classic deep blue and consistent tone. The fabric surface of overdyed denim tends to exhibit subtle tonal variations and a slightly softer hand feel due to the extra dyeing process, while traditional indigo denim remains stiffer with a more uniform texture owing to its raw or minimally washed treatment. These differences influence the garment's aesthetic appeal, with overdyed denim offering a contemporary, artisanal look and traditional indigo denim maintaining a timeless, rugged character.
Durability and Longevity: Overdyed vs Indigo Denim
Overdyed denim undergoes an extra dyeing process that can sometimes weaken fabric fibers compared to traditional indigo denim, which retains its original strength. Traditional indigo denim is known for its exceptional durability due to its natural dyeing method and less chemical processing. When considering longevity, indigo denim tends to maintain structural integrity and color fade gradually, whereas overdyed denim may show signs of wear and color loss more quickly.
Fading Patterns: What to Expect
Overdyed denim displays more uniform fading with vibrant, saturated hues that gradually lighten, creating a bold and modern worn-in look. Traditional indigo denim develops natural, high-contrast fades along stress points such as knees, thighs, and pockets, resulting in classic blue-to-white wear patterns. Expect overdyed denim to maintain deeper color intensity over time, while traditional indigo fades emphasize texture and character through varied shading.
Color Variety and Depth in Both Denims
Overdyed denim offers a broader and more vibrant color palette compared to traditional indigo denim, which primarily features deep blue hues. The overdying process enhances color depth by layering additional pigments, resulting in rich, saturated tones that evolve with wear. In contrast, traditional indigo denim develops subtle color fading and whiskering patterns over time, highlighting its natural dyeing process and creating a classic, textured appearance.
Environmental Impact of Dye Techniques
Overdyed denim uses post-production dyes, often synthetic, which may increase water and chemical consumption compared to traditional indigo dyeing that relies on natural or synthetic indigo with established water recycling methods. Traditional indigo dyeing typically involves multiple dips in dye baths, but innovations in eco-friendly indigo and closed-loop systems reduce water waste and chemical discharge significantly. Evaluating environmental impact requires considering wastewater treatment, chemical toxicity, and resource efficiency, where overdyed denim can pose higher ecological risks without stringent process controls.
Styling Versatility: When to Choose Which Denim
Overdyed denim offers a bold, vibrant aesthetic perfect for contemporary, statement-making outfits, ideal for casual wear or fashion-forward settings. Traditional indigo denim provides a classic, timeless appeal that suits a wide range of styles, from smart-casual to rugged, making it a versatile wardrobe staple. Choose overdyed denim to add color and personality, while traditional indigo denim remains the go-to for enduring style and adaptability.
Care and Maintenance for Each Denim Type
Overdyed denim requires gentle washing with cold water and minimal detergent to preserve the vibrant colors and avoid fading, while traditional indigo denim benefits from infrequent washing and air drying to maintain its deep blue hue and natural aging. Avoid harsh chemicals and bleach for both types, as they can degrade the fabric and alter the dye. Proper maintenance extends the lifespan of overdyed and traditional indigo denim, ensuring durability and color retention.
Price Factors and Market Accessibility
Overdyed denim typically commands a higher price due to its labor-intensive production process, which involves additional dyeing and finishing techniques to achieve unique color variations not found in traditional indigo denim. Traditional indigo denim benefits from mass production efficiencies and well-established supply chains, making it more accessible and affordable in mainstream markets. Market accessibility for overdyed denim remains limited primarily to niche segments and premium retailers, whereas traditional indigo denim is widely available across fast fashion and mid-tier brands.
Overdyed Denim vs Traditional Indigo Denim Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com