Indigo dyeing imparts a rich, deep blue color to denim fabric through a natural oxidation process that allows for unique fading and a vintage look. Sulphur dyeing offers an alternative palette, producing black, gray, and other dark shades with enhanced colorfastness and resistance to fading. Both dyeing methods influence denim's aesthetic and wear characteristics, making the choice essential for achieving specific design and durability goals.
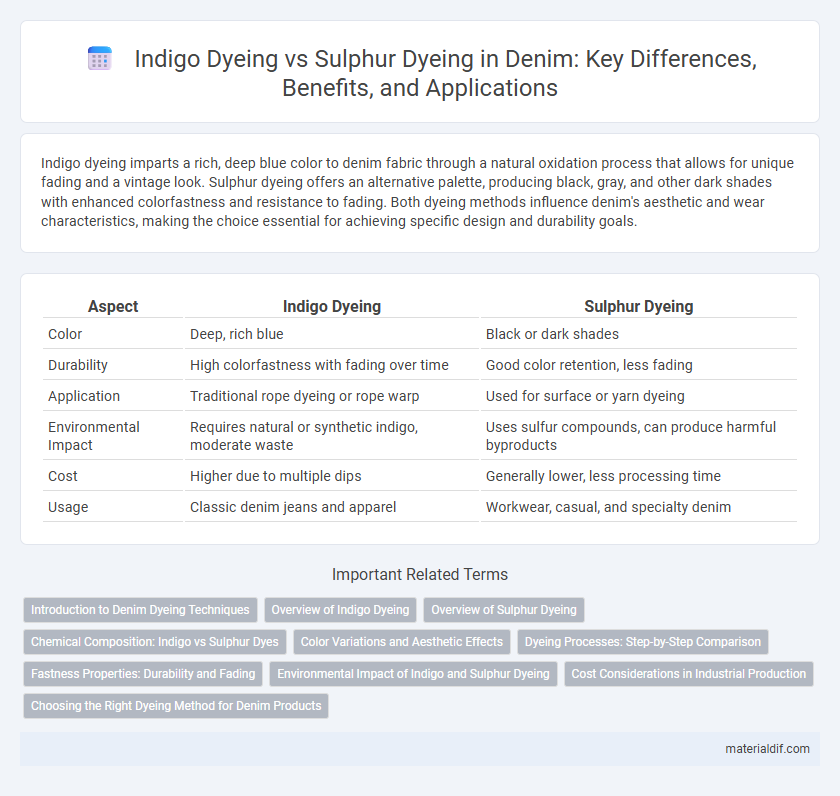
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Indigo Dyeing | Sulphur Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Color | Deep, rich blue | Black or dark shades |
| Durability | High colorfastness with fading over time | Good color retention, less fading |
| Application | Traditional rope dyeing or rope warp | Used for surface or yarn dyeing |
| Environmental Impact | Requires natural or synthetic indigo, moderate waste | Uses sulfur compounds, can produce harmful byproducts |
| Cost | Higher due to multiple dips | Generally lower, less processing time |
| Usage | Classic denim jeans and apparel | Workwear, casual, and specialty denim |
Introduction to Denim Dyeing Techniques
Indigo dyeing is the traditional method used in denim manufacturing, known for its unique fading properties and ability to create the classic blue color through a vat dyeing process. Sulphur dyeing offers a versatile alternative, producing a range of colors including black, white, and green by bonding sulfur compounds to the fabric, enhancing colorfastness and durability. These techniques define denim's visual appeal and performance characteristics in fashion and workwear industries.
Overview of Indigo Dyeing
Indigo dyeing is the traditional method used in denim production, renowned for its unique fading properties and rich blue hues derived from natural or synthetic indigo pigments. This dyeing process involves repeatedly dipping yarns into an indigo dye bath, allowing oxidation to develop the characteristic deep blue color, which gradually fades with wear and washing to create denim's iconic look. Unlike sulphur dyeing, which produces black or grey tones, indigo offers greater color depth and vintage appeal central to classic denim aesthetics.
Overview of Sulphur Dyeing
Sulphur dyeing in denim production involves using sulphur-based compounds to achieve deep black or gray hues with excellent colorfastness and minimal fading. This method provides cost-effective dyeing solutions while offering resistance to abrasion and light exposure, making it ideal for rugged denim applications. Unlike indigo dyeing, which creates a distinctive fading effect through surface dyeing, sulphur dyeing penetrates the fabric for uniform and durable coloration.
Chemical Composition: Indigo vs Sulphur Dyes
Indigo dyeing relies on the chemical compound indigotin, a natural or synthetic pigment that provides deep blue hues through a reduction-oxidation process enabling fibers to absorb the dye in its soluble form before oxidation fixes the color. Sulphur dyes, composed primarily of complex sulfur-containing compounds such as thiophenes and sulfides, create a range of dark shades including black and brown by bonding to cellulose fibers through a reduction process and subsequent oxidation. Indigo offers a characteristic vibrant blue with high wash-fastness, while Sulphur dyes achieve earthy tones with cost-effective, durable coloring suited for diverse denim finishes.
Color Variations and Aesthetic Effects
Indigo dyeing produces classic deep blue shades with unique fading characteristics that enhance the vintage aesthetic of denim, creating a rich, textured look over time. Sulphur dyeing offers a broader palette ranging from black to brown and grey tones, providing bold color variations suited for modern and fashion-forward denim styles. The combination of these dyeing techniques allows designers to achieve distinctive finishes, enriching denim's visual appeal through diverse color depth and surface effects.
Dyeing Processes: Step-by-Step Comparison
Indigo dyeing involves a complex oxidation process where yarn is repeatedly dipped into a vat of reduced indigo solution, then exposed to air to develop its characteristic blue hue through chemical oxidation. In contrast, sulphur dyeing uses a thermal reduction method, where yarn is treated with sulfur-based dyes in a hot alkaline bath, producing a wide range of colors from black to dark shades but with less wash-fastness compared to indigo. Both processes require multiple stages of rinsing and drying, but indigo dyeing is renowned for its unique fading properties and color depth, whereas sulphur dyeing offers cost-effective alternatives for darker denim finishes.
Fastness Properties: Durability and Fading
Indigo dyeing in denim provides superior fastness properties with enhanced durability and controlled fading due to the dye's insolubility and strong affinity for cotton fibers, resulting in a characteristic worn look over time. Sulphur dyeing offers excellent fastness but tends to deliver deeper, earth-toned colors with a quicker fading rate under extended UV exposure and washing, which can affect overall fabric longevity. The combination of indigo's gradual fading and sulphur's robust color retention is often leveraged to balance aesthetic appeal and durability in high-quality denim production.
Environmental Impact of Indigo and Sulphur Dyeing
Indigo dyeing typically requires large volumes of water and the use of chemical reducing agents, which can lead to significant water pollution if not properly treated. Sulphur dyeing, while less water-intensive, generates sulfur compounds that can cause environmental harm through air emissions and wastewater contamination. Proper effluent treatment and sustainable practices are essential in both methods to minimize their ecological footprint in denim production.
Cost Considerations in Industrial Production
Indigo dyeing in industrial denim production involves higher raw material costs due to the complex extraction and fermentation processes required, whereas sulphur dyeing offers a more economical alternative with faster application and lower chemical consumption. Sulphur dyes provide cost savings in equipment and energy usage as they require lower dyeing temperatures and shorter process times compared to indigo, which demands multiple dipping cycles to achieve desired shades. However, the choice between indigo and sulphur dyeing ultimately depends on balancing cost efficiencies against fabric quality and desired aesthetic effects in large-scale denim manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Dyeing Method for Denim Products
Indigo dyeing offers the classic deep blue hue and natural fading effects that aging denim enthusiasts seek, while sulphur dyeing provides a broader color range including black, brown, and olive with good colorfastness and cost efficiency. Selecting the right dyeing method depends on the desired aesthetic, fabric type, and production budget; indigo dyeing suits traditional, high-end denim requiring vintage appeal, whereas sulphur dyeing is ideal for mass production and varied color palettes. Understanding the technical properties and maintenance needs of each dyeing process ensures product durability and customer satisfaction in denim manufacturing.
Indigo dyeing vs Sulphur dyeing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com