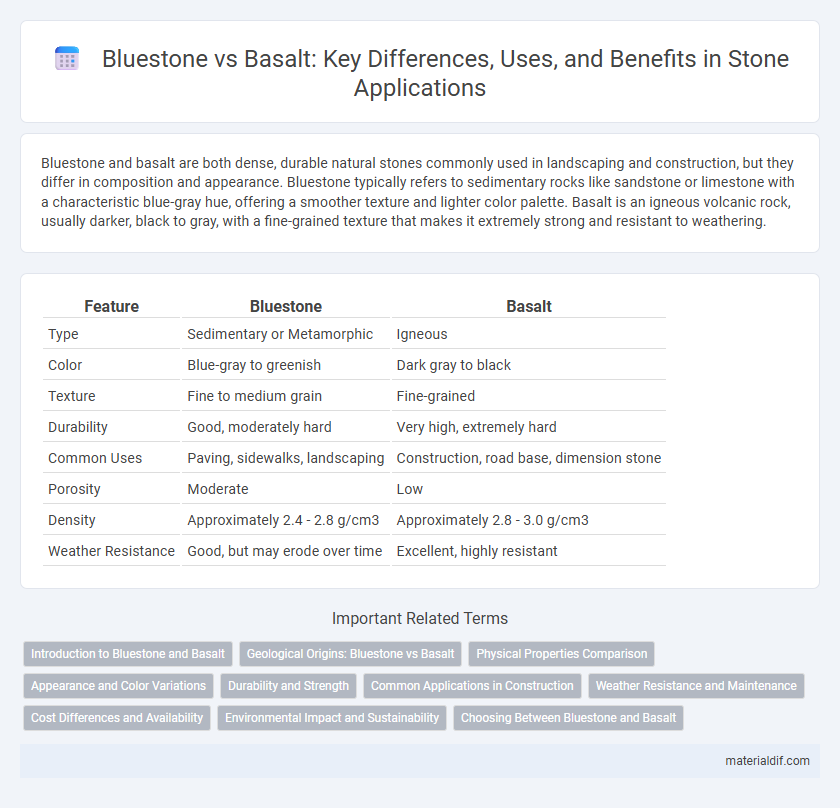
Bluestone and basalt are both dense, durable natural stones commonly used in landscaping and construction, but they differ in composition and appearance. Bluestone typically refers to sedimentary rocks like sandstone or limestone with a characteristic blue-gray hue, offering a smoother texture and lighter color palette. Basalt is an igneous volcanic rock, usually darker, black to gray, with a fine-grained texture that makes it extremely strong and resistant to weathering.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bluestone | Basalt |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Sedimentary or Metamorphic | Igneous |
| Color | Blue-gray to greenish | Dark gray to black |
| Texture | Fine to medium grain | Fine-grained |
| Durability | Good, moderately hard | Very high, extremely hard |
| Common Uses | Paving, sidewalks, landscaping | Construction, road base, dimension stone |
| Porosity | Moderate | Low |
| Density | Approximately 2.4 - 2.8 g/cm3 | Approximately 2.8 - 3.0 g/cm3 |
| Weather Resistance | Good, but may erode over time | Excellent, highly resistant |
Introduction to Bluestone and Basalt
Bluestone is a dense, fine-grained sandstone commonly found in the northeastern United States, prized for its durability and distinctive blue-gray hue. Basalt is an igneous volcanic rock characterized by its dark color and fine texture, formed from rapid cooling of basaltic lava. Both stones are popular in construction and landscaping due to their strength and aesthetic appeal, but their differing geological origins influence their physical properties and applications.
Geological Origins: Bluestone vs Basalt
Bluestone originates from sedimentary rock formations, primarily composed of sandstone or shale, formed through the compression of sediment layers over millions of years. Basalt is an igneous rock created from the rapid cooling of basaltic lava flows, resulting in a dense, fine-grained texture. The geological differences between bluestone and basalt influence their durability, appearance, and suitability for construction and landscaping applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Bluestone exhibits a medium hardness with a Mohs scale rating around 6, making it moderately durable and suitable for various construction purposes. Basalt, with a higher Mohs hardness of approximately 6 to 7, offers greater density and strength, resulting in superior resistance to abrasion and weathering. Bluestone typically has a lighter color and finer grain compared to the darker, coarse-grained texture of basalt, influencing both aesthetic appeal and performance in outdoor applications.
Appearance and Color Variations
Bluestone typically exhibits a range of blue-gray hues with subtle variations that create a more uniform and muted appearance, making it popular for patios and walkways. Basalt, on the other hand, features a darker, almost black color with a fine-grained texture and occasional speckles or veins, offering a striking contrast and more dramatic visual impact. Both stones provide durability but differ significantly in aesthetic qualities, with bluestone's softer tones complementing natural landscapes and basalt's bold colors enhancing modern architectural designs.
Durability and Strength
Bluestone exhibits moderate durability with a fine-grained texture that resists weathering, making it suitable for outdoor applications like patios and walkways. Basalt, an igneous volcanic rock, offers superior strength and exceptional hardness due to its dense crystalline structure, resulting in higher resistance to abrasion and impact. While both stones perform well under heavy use, basalt's enhanced durability makes it ideal for high-traffic surfaces and structural components requiring long-lasting strength.
Common Applications in Construction
Bluestone is commonly used in patios, walkways, and garden walls due to its natural cleft surface and attractive blue-gray color, providing durable and slip-resistant flooring. Basalt, known for its high density and strength, is frequently employed in structural applications like building blocks, road base, and bridge supports, offering exceptional load-bearing capacity. Both stones are favored in construction for their weather resistance and longevity, but bluestone is preferred for aesthetic landscaping while basalt excels in heavy-duty infrastructure projects.
Weather Resistance and Maintenance
Bluestone exhibits excellent weather resistance due to its dense composition, making it highly durable against freeze-thaw cycles and moisture penetration. Basalt also offers strong weather resistance, with its fine-grained texture reducing water absorption and preventing surface erosion. Both stones require minimal maintenance; however, bluestone may benefit from periodic sealing to preserve its appearance, while basalt's natural hardness typically demands less frequent upkeep.
Cost Differences and Availability
Bluestone generally costs less than basalt due to its wider availability and easier quarrying processes, making it a more budget-friendly option for landscaping and construction projects. Basalt, being denser and harder to extract, often commands higher prices and may have limited supply depending on geographic location. Availability of bluestone is more consistent across regions in the United States, while basalt is more commonly sourced from volcanic areas, impacting transportation costs and overall affordability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bluestone and basalt differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability, with bluestone often sourced from sedimentary deposits requiring intensive quarrying, leading to higher habitat disruption. Basalt, an igneous rock, tends to be more abundant and extracted with lower ecological footprint due to its widespread availability and efficient quarrying methods. The durability and natural longevity of basalt contribute to sustainable construction practices by reducing the need for frequent replacement and minimizing resource consumption.
Choosing Between Bluestone and Basalt
Choosing between bluestone and basalt depends on project requirements such as durability, appearance, and budget. Bluestone offers a smoother texture and a range of blue-gray hues ideal for patios and walkways, while basalt is denser and darker, providing superior hardness and resistance to weathering. Consider bluestone for aesthetic appeal and versatility, and basalt for heavy-duty applications requiring maximum strength and longevity.
Bluestone vs Basalt Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com