Linen flax fiber is derived from the flax plant and is known for its strength, smooth texture, and breathability, making it ideal for high-quality textiles and apparel. Jute fiber, extracted from the jute plant, is coarser and more durable, often used in making sacks, ropes, and eco-friendly packaging materials. Both fibers are biodegradable and sustainable, but linen offers superior softness and moisture-wicking properties compared to the rougher, more rigid jute.
Table of Comparison
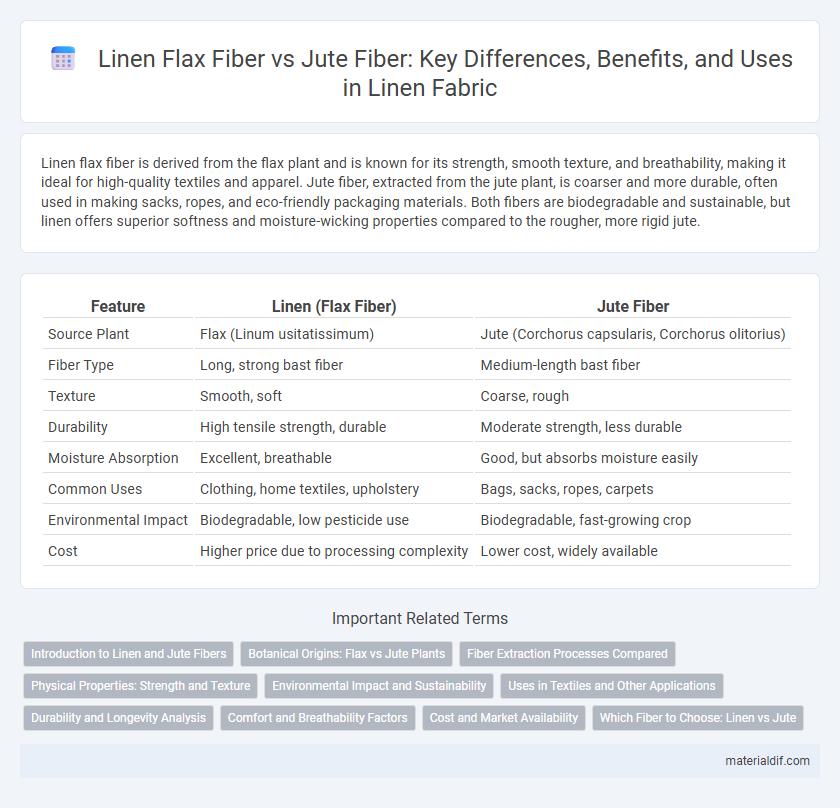
| Feature | Linen (Flax Fiber) | Jute Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source Plant | Flax (Linum usitatissimum) | Jute (Corchorus capsularis, Corchorus olitorius) |
| Fiber Type | Long, strong bast fiber | Medium-length bast fiber |
| Texture | Smooth, soft | Coarse, rough |
| Durability | High tensile strength, durable | Moderate strength, less durable |
| Moisture Absorption | Excellent, breathable | Good, but absorbs moisture easily |
| Common Uses | Clothing, home textiles, upholstery | Bags, sacks, ropes, carpets |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low pesticide use | Biodegradable, fast-growing crop |
| Cost | Higher price due to processing complexity | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Linen and Jute Fibers
Linen flax fiber, derived from the flax plant, is renowned for its strength, durability, and smooth texture, making it a preferred choice for high-quality textiles and eco-friendly fabrics. Jute fiber, sourced from the jute plant primarily grown in South Asia, is coarse and less durable but highly valued for its affordability, biodegradability, and use in packaging, sacks, and ropes. Both fibers are natural, renewable resources with distinct applications based on their physical properties and environmental benefits.
Botanical Origins: Flax vs Jute Plants
Linen flax fiber derives from the stems of the flax plant (Linum usitatissimum), known for its fine, strong fibers ideal for high-quality textiles. In contrast, jute fiber is obtained from the outer bast of the jute plant (Corchorus species), characterized by coarser texture and rapid growth suitable for industrial uses like sacks and ropes. The botanical differences between flax and jute influence fiber properties, cultivation requirements, and end-use applications in the textile industry.
Fiber Extraction Processes Compared
Linen flax fiber and jute fiber differ significantly in their extraction processes, impacting fiber quality and application. Linen flax undergoes retting, a microbial process that separates fibers from the woody stem by breaking down pectin, followed by scutching and hackling to remove impurities and align fibers, producing long, smooth, and strong fibers ideal for fine textiles. In contrast, jute extraction primarily involves water retting, which softens the stem and loosens fibers, but the process yields coarser, shorter fibers typically used in sacks, ropes, and coarse fabrics.
Physical Properties: Strength and Texture
Linen flax fiber exhibits superior tensile strength compared to jute fiber, making it more durable and resistant to wear. Its smooth, fine texture provides a soft feel ideal for high-quality textiles, whereas jute fiber is coarser and rougher, commonly used for sacks and ropes. The tightly packed fiber structure of flax results in greater flexibility and resilience, distinguishing it from the bulkier, less elastic jute fibers.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Linen flax fiber is derived from the flax plant, requiring less water and fewer pesticides compared to jute fiber, which grows quickly but often demands more chemical inputs for pest control. Flax fibers are biodegradable and have a lower carbon footprint due to sustainable farming practices, making linen a more eco-friendly choice. Jute fiber, while renewable and widely used in packaging and textiles, tends to have a higher environmental impact due to intensive cultivation methods and less efficient water use.
Uses in Textiles and Other Applications
Linen flax fiber is prized in textiles for its strength, smooth texture, and breathability, making it ideal for high-quality apparel, bed linens, and upholstery. Jute fiber, although coarser and less durable, excels in producing eco-friendly sacks, ropes, and carpets, with growing use in geotextiles and composite materials. Both fibers support sustainable industries, but linen's versatility favors finer textile applications while jute dominates packaging and industrial uses.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Linen flax fiber exhibits superior durability compared to jute fiber due to its long, strong cellulose fibers that resist wear and tear. The intrinsic strength of linen contributes to its longevity, making it ideal for high-quality textiles and upholstery that require extended use. In contrast, jute fiber, while economical and biodegradable, tends to degrade faster under moisture and friction, limiting its lifespan in heavy-duty applications.
Comfort and Breathability Factors
Linen flax fiber offers superior comfort and breathability compared to jute fiber due to its finer and smoother texture, which enhances moisture-wicking properties and air circulation. The natural cellulose structure in flax fibers allows for better thermal regulation, keeping fabrics cool in warm weather and dry by absorbing sweat efficiently. In contrast, jute fiber tends to be coarser and less flexible, resulting in reduced softness and limited breathability, making linen a preferred choice for comfortable, breathable textiles.
Cost and Market Availability
Linen flax fiber generally commands a higher price than jute fiber due to its superior strength, durability, and finer texture, making it favored in premium textile markets. Jute fiber offers a more affordable option with widespread availability, especially in regions like India and Bangladesh where production is high and infrastructure supports large-scale export. Market availability trends show jute dominating bulk industrial applications, while linen remains niche for luxury and specialty fabrics, influencing cost dynamics accordingly.
Which Fiber to Choose: Linen vs Jute
Linen flax fiber is valued for its strength, smooth texture, and breathability, making it ideal for high-quality textiles and apparel. Jute fiber, while coarser and less durable, excels in eco-friendly packaging, rugs, and sacks due to its cost-effectiveness and biodegradability. Choosing between linen and jute depends on the application's need for durability, texture, and environmental impact, with linen preferred for fine fabrics and jute suited for industrial uses.
Linen Flax Fiber vs Jute Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com