Tweed features a rough, woolen texture with a variety of colored yarns woven together to create a heathered or checked pattern, ideal for warmth and durability. Herringbone uses a distinctive V-shaped weaving pattern resembling fish bones, offering a more refined and structured appearance often found in suits and outerwear. Both fabrics provide excellent insulation but differ in pattern complexity and overall aesthetic appeal.
Table of Comparison
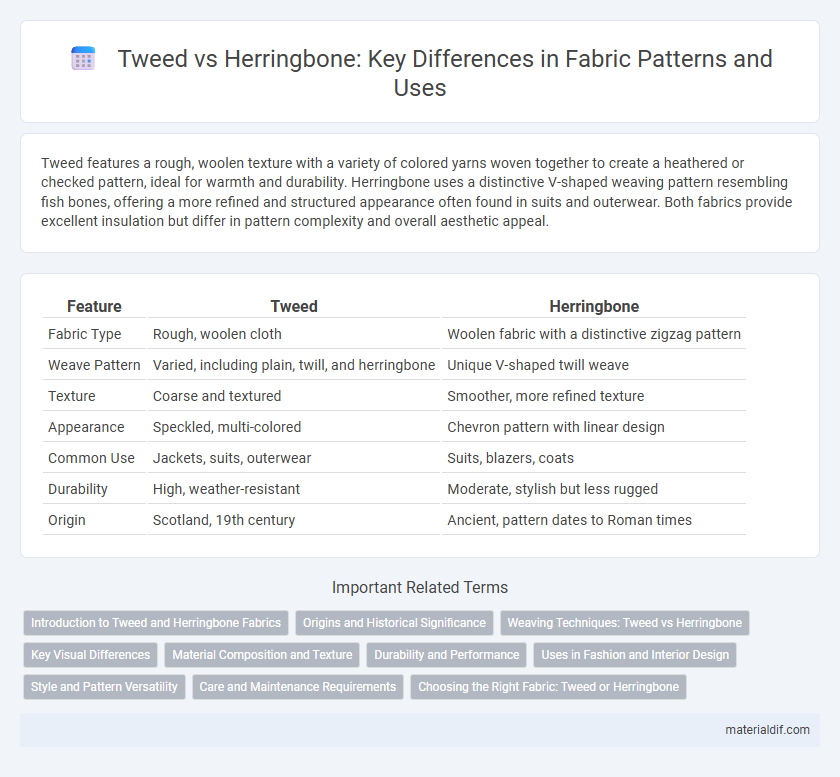
| Feature | Tweed | Herringbone |
|---|---|---|
| Fabric Type | Rough, woolen cloth | Woolen fabric with a distinctive zigzag pattern |
| Weave Pattern | Varied, including plain, twill, and herringbone | Unique V-shaped twill weave |
| Texture | Coarse and textured | Smoother, more refined texture |
| Appearance | Speckled, multi-colored | Chevron pattern with linear design |
| Common Use | Jackets, suits, outerwear | Suits, blazers, coats |
| Durability | High, weather-resistant | Moderate, stylish but less rugged |
| Origin | Scotland, 19th century | Ancient, pattern dates to Roman times |
Introduction to Tweed and Herringbone Fabrics
Tweed fabric is a rough, woolen material known for its durability and moisture resistance, traditionally used in outdoor and country clothing. Herringbone fabric features a distinctive V-shaped weaving pattern, creating a zigzag effect that adds texture and visual interest to wool or tweed textiles. Both fabrics are prized for their warmth and sturdiness, with tweed emphasizing rugged, rustic charm and herringbone offering refined, geometric sophistication.
Origins and Historical Significance
Tweed fabric originated in Scotland during the 18th century, known for its durability and warmth, making it ideal for outdoor wear among the British aristocracy. Herringbone, a distinct twill weave pattern, also developed in Europe, with roots tracing back to ancient Roman times, symbolizing craftsmanship and sophistication. Both fabrics hold strong historical significance, with tweed representing rugged country estates and herringbone embodying refined urban tailoring traditions.
Weaving Techniques: Tweed vs Herringbone
Tweed is a coarse woolen fabric characterized by a plain or twill weave incorporating irregular flecks of color, creating a textured, rustic appearance. Herringbone, distinguished by its distinctive V-shaped weaving pattern, produces a smooth, elegant fabric with a firm hand and subtle zigzag design. Both fabrics rely on wool fibers but differ significantly in weaving technique, with Tweed focusing on random, multicolored yarns and Herringbone emphasizing geometric precision in its weave structure.
Key Visual Differences
Tweed fabric is characterized by its rough, woolen texture and multi-colored flecks, offering a rustic, textured appearance that's ideal for outerwear. Herringbone, a distinctive V-shaped weave pattern, features a smooth, zigzag design often found in wool or cotton, lending a refined, structured look to suiting and jackets. Key visual differences include Tweed's speckled, bulky texture versus Herringbone's clean, repetitive chevron pattern enhancing fabric symmetry and elegance.
Material Composition and Texture
Tweed fabric is traditionally composed of wool with a coarse, rough texture that offers warmth and durability, making it ideal for outerwear. Herringbone fabric also uses wool but features a distinctive V-shaped weaving pattern that creates a smoother, more refined texture with subtle ridges. Both fabrics are prized for their robustness, but tweed's varied thread colors provide a more rustic appearance, while herringbone is known for its elegant, symmetrical design.
Durability and Performance
Tweed offers exceptional durability due to its tightly woven, coarse wool fibers, making it highly resistant to wear and ideal for outdoor use. Herringbone, characterized by its distinctive V-shaped weave, provides excellent performance with added flexibility and breathability, enhancing comfort during prolonged wear. Both fabrics excel in strength, but tweed's rugged texture ensures superior longevity in harsh conditions while herringbone balances durability with a refined, lightweight structure.
Uses in Fashion and Interior Design
Tweed fabric, known for its coarse texture and warmth, is extensively used in fashion for durable outerwear like jackets and coats, as well as rustic-inspired accessories. Herringbone, characterized by its distinctive V-shaped weaving pattern, is favored in both fashion and interior design for sophisticated suits, scarves, upholstery, and accent pillows, adding a touch of elegance and subtle pattern. While tweed lends a rugged, traditional look ideal for country wear and cozy interiors, herringbone's refined geometric structure enhances modern and classic aesthetics across garments and home decor.
Style and Pattern Versatility
Tweed offers a rustic, textured look with a dense weave ideal for classic, rugged styles, while herringbone showcases a distinctive V-shaped zigzag pattern that lends itself to more refined, sophisticated attire. Tweed's versatility spans from casual outerwear to stylish suits, complementing earthy tones and natural fabrics. Herringbone's pattern adaptability enhances both formal and casual garments, providing a timeless yet modern aesthetic suitable for diverse fashion contexts.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
Tweed fabric requires gentle care, typically dry cleaning, to preserve its texture and color while avoiding shrinkage and distortion. Herringbone, often made from wool blends, needs careful brushing and airing to prevent moth damage and maintain its distinctive pattern. Both fabrics benefit from storage in breathable garment bags and minimal exposure to moisture to extend their longevity.
Choosing the Right Fabric: Tweed or Herringbone
Tweed fabric is characterized by its rough texture and multicolored flecks, making it ideal for rugged outerwear and casual jackets that require durability and warmth. Herringbone features a distinctive V-shaped weaving pattern that offers a refined, lightweight option suitable for tailored suits and formal wear. Choosing between tweed and herringbone depends on the desired balance of texture, pattern sophistication, and functional use in your wardrobe.
Tweed vs Herringbone Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com