Acrylic fibers are synthetic, offering excellent durability, colorfastness, and resistance to wrinkles and sunlight, making them ideal for outdoor and activewear fabrics. Acetate fibers, derived from cellulose, provide a silky appearance and smooth texture, often used in linings and formal wear due to their lustrous finish and breathability. Choosing between acrylic and acetate depends on the desired balance of strength, appearance, and comfort for specific fabric applications.
Table of Comparison
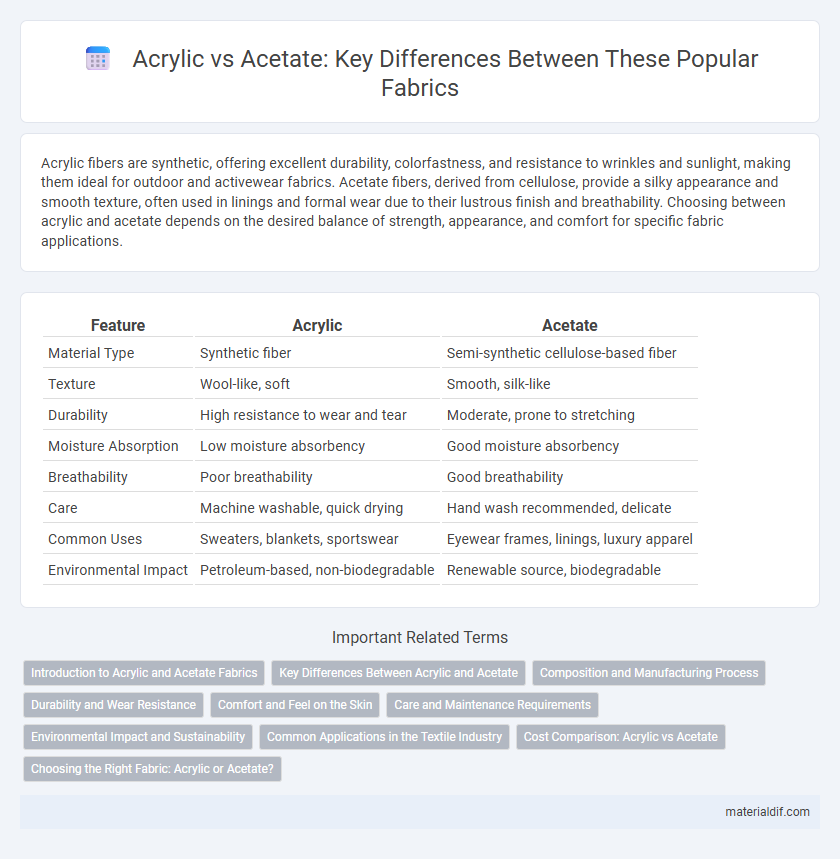
| Feature | Acrylic | Acetate |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic fiber | Semi-synthetic cellulose-based fiber |
| Texture | Wool-like, soft | Smooth, silk-like |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and tear | Moderate, prone to stretching |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorbency | Good moisture absorbency |
| Breathability | Poor breathability | Good breathability |
| Care | Machine washable, quick drying | Hand wash recommended, delicate |
| Common Uses | Sweaters, blankets, sportswear | Eyewear frames, linings, luxury apparel |
| Environmental Impact | Petroleum-based, non-biodegradable | Renewable source, biodegradable |
Introduction to Acrylic and Acetate Fabrics
Acrylic fabric is a synthetic textile made from polymer fibers known for its lightweight, soft texture, and excellent resistance to sunlight and moisture, making it suitable for outdoor use and activewear. Acetate fabric, derived from cellulose fibers through chemical modification with acetic anhydride, offers a silky appearance and luxurious drape, often used in linings, formal wear, and lingerie. Both acrylic and acetate serve distinct purposes due to their unique properties: acrylic excels in durability and color retention, while acetate provides a smooth finish and elegant sheen.
Key Differences Between Acrylic and Acetate
Acrylic fabric is a synthetic polymer known for its wool-like feel, high durability, and resistance to moisture and UV damage, making it ideal for outdoor use. Acetate fiber, derived from cellulose, offers a silky appearance and excellent drape but lacks the strength and moisture resistance of acrylic. Key differences include acrylic's superior thermal insulation and abrasion resistance compared to acetate's delicate nature and sensitivity to heat.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Acrylic fabric is made from synthetic polymer fibers derived from polyacrylonitrile through a process called polymerization, resulting in a wool-like texture with excellent durability and color retention. Acetate fabric is produced from cellulose acetate, a chemically modified natural cellulose obtained from wood pulp or cotton linters, using an acetylation process that imparts a silky appearance and good drape. The manufacturing process of acrylic involves polymer extrusion and fiber spinning, while acetate involves dissolving cellulose in an acetylating agent followed by fiber formation, leading to distinct properties in texture, feel, and performance.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Acrylic fabric offers excellent durability and wear resistance due to its strong synthetic fibers that resist abrasion, fading, and moisture, making it ideal for outdoor and heavy-use applications. Acetate, while smooth and luxurious in appearance, tends to be less durable and more prone to wear, including pilling and stretching, limiting its suitability for high-friction environments. The inherent strength of acrylic fibers significantly outperforms acetate in maintaining fabric integrity and appearance over extended periods.
Comfort and Feel on the Skin
Acrylic fabric offers a soft texture but can feel slightly synthetic and less breathable on the skin, often causing discomfort during extended wear. Acetate provides a smooth, silk-like feel with better moisture absorption, enhancing comfort and reducing irritation. For sensitive skin, acetate is generally preferred due to its breathable nature and gentle touch.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
Acrylic fabric requires low-maintenance care, typically involving gentle machine washing in cold water and air drying to prevent shrinking or distortion. Acetate fabric demands more delicate handling, including dry cleaning or hand washing with mild detergent, as it is prone to damage from heat and water exposure. Proper care of acrylic extends fabric lifespan due to its durability, while acetate's sensitivity necessitates cautious maintenance to avoid fiber weakening and surface pilling.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Acrylic fabric is derived from petroleum-based polymers, making it less sustainable due to its non-biodegradable nature and high energy consumption during production, contributing significantly to carbon emissions. Acetate, produced from cellulose fibers derived from wood pulp, offers a more eco-friendly alternative as it is partially biodegradable and sourced from renewable materials, though chemical processing can impact environmental safety. Choosing acetate can reduce environmental footprint compared to acrylic, but both materials require consideration of production methods and end-of-life disposal for true sustainability.
Common Applications in the Textile Industry
Acrylic fibers are widely used in textiles for sweaters, blankets, and sportswear due to their warmth, durability, and resistance to moisture and UV light. Acetate fibers, prized for their silk-like luster and smooth texture, are commonly employed in linings, formal wear, and draperies to enhance aesthetic appeal and comfort. Both fibers serve distinct roles in the textile industry, with acrylic favored for performance and acetate for elegance.
Cost Comparison: Acrylic vs Acetate
Acrylic fabric generally costs less than acetate, making it a budget-friendly choice for many textile applications. Acrylic fibers offer durability and colorfastness at a lower price point, while acetate, being more expensive, provides a luxurious sheen and better drape. The cost difference is influenced by the production process and raw material prices, with acetate's higher manufacturing expense reflected in retail prices.
Choosing the Right Fabric: Acrylic or Acetate?
Acrylic fabric offers excellent warmth, durability, and resistance to moths and sunlight, making it ideal for sweaters and outdoor garments. Acetate fabric provides a silky appearance with excellent drape and moisture absorption, suited for linings and formal wear. Choosing between acrylic and acetate depends on the desired fabric performance, care requirements, and end-use application.
Acrylic vs Acetate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com