Microfiber fabric is finely woven to create a lightweight, breathable material known for its moisture-wicking and quick-drying properties, making it ideal for activewear and performance gear. Fleece, made from synthetic fibers like polyester, offers exceptional warmth and softness with a thicker, plush texture that excels in insulation and comfort during cold weather. While microfiber excels in moisture management and durability, fleece is preferred for its cozy feel and superior heat retention.
Table of Comparison
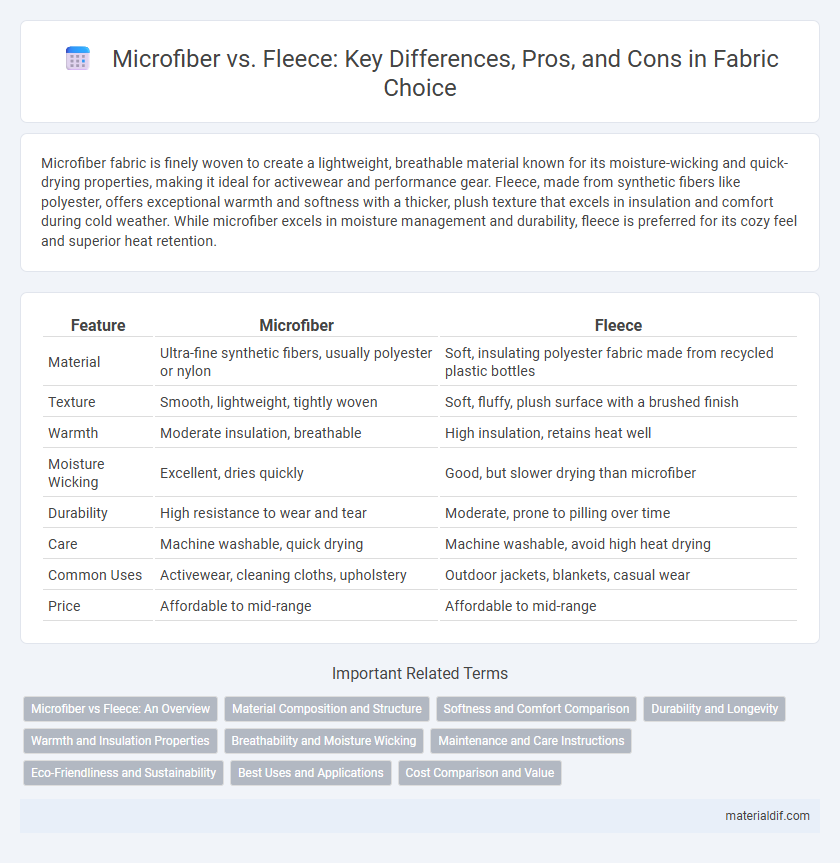
| Feature | Microfiber | Fleece |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Ultra-fine synthetic fibers, usually polyester or nylon | Soft, insulating polyester fabric made from recycled plastic bottles |
| Texture | Smooth, lightweight, tightly woven | Soft, fluffy, plush surface with a brushed finish |
| Warmth | Moderate insulation, breathable | High insulation, retains heat well |
| Moisture Wicking | Excellent, dries quickly | Good, but slower drying than microfiber |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and tear | Moderate, prone to pilling over time |
| Care | Machine washable, quick drying | Machine washable, avoid high heat drying |
| Common Uses | Activewear, cleaning cloths, upholstery | Outdoor jackets, blankets, casual wear |
| Price | Affordable to mid-range | Affordable to mid-range |
Microfiber vs Fleece: An Overview
Microfiber fabric consists of ultra-fine synthetic fibers, typically made from polyester or nylon, providing exceptional softness, durability, and moisture-wicking properties compared to fleece. Fleece is a knit fabric usually made from polyester, designed for warmth and insulation, featuring a brushed texture that traps heat effectively. Microfiber excels in breathability and quick drying, while fleece is preferred for thermal comfort in cold conditions.
Material Composition and Structure
Microfiber fabric consists of ultra-fine synthetic fibers, typically polyester or nylon, woven tightly to create a smooth, lightweight texture that offers high durability and moisture-wicking properties. Fleece is made from loosely knit or woven polyester fibers brushed to create a thick, plush structure that traps air, providing excellent insulation and warmth. The structural differences in microfiber's dense weave versus fleece's lofted pile directly impact their breathability and thermal retention capabilities.
Softness and Comfort Comparison
Microfiber fabric offers exceptional softness due to its fine synthetic fibers, creating a smooth, lightweight texture that feels gentle against the skin. Fleece, typically made from polyester, provides superior warmth and a plush, cozy comfort with a thicker, loftier texture ideal for cold weather. While microfiber excels in breathability and moisture-wicking for active comfort, fleece delivers enhanced insulation and a soft, fuzzy surface perfect for layering during colder seasons.
Durability and Longevity
Microfiber fabric boasts superior durability due to its tightly woven fibers, resisting wear and tear better than fleece. Fleece, while softer and warmer, tends to pill and degrade faster with frequent washing and heavy use. For long-lasting garments or upholstery, microfiber offers enhanced longevity and maintains its appearance over time.
Warmth and Insulation Properties
Microfiber fabric offers excellent warmth by trapping heat within its densely woven fibers, providing lightweight insulation suitable for mild to moderately cold conditions. Fleece excels in insulation due to its thicker pile and air-trapping capabilities, making it ideal for retaining body heat in colder environments. While microfiber is breathable and quick-drying, fleece provides superior warmth retention and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing overall comfort in cold weather.
Breathability and Moisture Wicking
Microfiber fabric excels in breathability due to its fine fibers that allow air circulation while effectively wicking moisture away from the skin, keeping the wearer dry and comfortable. Fleece, though warm and soft, typically offers lower breathability but provides decent moisture-wicking properties by drawing sweat from the body to the outer surface for quicker evaporation. For activities requiring enhanced ventilation and moisture management, microfiber is often preferred, whereas fleece suits colder conditions with moderate moisture control.
Maintenance and Care Instructions
Microfiber fabric requires gentle washing with mild detergent and cold water to maintain its softness and avoid damage to its fine fibers, while fleece demands regular washing in cold water using a gentle cycle to preserve its insulating properties and prevent pilling. Both fabrics benefit from air drying or tumble drying on low heat to extend their lifespan and prevent shrinking or fiber distortion. Avoiding fabric softeners and bleach is essential for both microfiber and fleece to retain their texture and performance over time.
Eco-Friendliness and Sustainability
Microfiber and fleece differ significantly in eco-friendliness and sustainability, with microfiber often made from non-biodegradable synthetic fibers like polyester and nylon, contributing to microplastic pollution. Fleece, typically derived from recycled plastics such as PET bottles, offers a more sustainable option by repurposing waste materials and reducing landfill impact. However, both fabrics shed microfibers during washing, impacting aquatic ecosystems, thus making responsible production and care essential for minimizing environmental harm.
Best Uses and Applications
Microfiber excels in activewear and sports apparel due to its lightweight, moisture-wicking properties and durability, making it ideal for high-performance use. Fleece is best suited for cold-weather clothing and outdoor gear, providing superior insulation and warmth with a soft, breathable texture. Both fabrics serve distinct purposes: microfiber for moisture management and flexibility, fleece for thermal comfort and cozy layering.
Cost Comparison and Value
Microfiber fabric generally costs more than fleece due to its finer fibers and advanced manufacturing process, but offers superior softness, moisture-wicking properties, and durability. Fleece is more affordable and provides excellent warmth and breathability, making it a cost-effective option for casual wear and outdoor activities. Evaluating long-term value, microfiber's resilience and performance often justify its higher initial price, while fleece represents budget-friendly comfort.
Microfiber vs Fleece Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com